_targeting Bcl-2-IP3 receptor interaction to treat cancer: A novel approach inspired by nearly a century treating cancer with adrenal corticosteroid hormones
- PMID: 30053503
- PMCID: PMC6345611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.07.020
_targeting Bcl-2-IP3 receptor interaction to treat cancer: A novel approach inspired by nearly a century treating cancer with adrenal corticosteroid hormones
Abstract
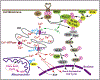
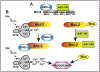
Bcl-2 inhibits cell death by at least two different mechanisms. On the one hand, its BH3 domain binds to pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bim and prevents apoptosis induction. On the other hand, the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 binds to the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R), preventing Ca2+ signals that mediate cell death. In normal T-cells, Bcl-2 levels increase during the immune response, protecting against cell death, and then decline as apoptosis ensues and the immune response dissipates. But in many cancers Bcl-2 is aberrantly expressed and exploited to prevent cell death by inhibiting IP3R-mediated Ca2+ elevation. This review summarizes what is known about the mechanism of Bcl-2's control over IP3R-mediated Ca2+ release and cell death induction. Early insights into the role of Ca2+ elevation in corticosteroid-mediated cell death serves as a model for how _targeting IP3R-mediated Ca2+ elevation can be a highly effective therapeutic approach for different types of cancer. Moreover, the successful development of ABT-199 (Venetoclax), a small molecule _targeting the BH3 domain of Bcl-2 but without effects on Ca2+, serves as proof of principle that _targeting Bcl-2 can be an effective therapeutic approach. BIRD-2, a synthetic peptide that inhibits Bcl-2-IP3R interaction, induces cell death induction in ABT-199 (Venetoclax)-resistant cancer models, attesting to the value of developing therapeutic agents that selectively _target Bcl-2-IP3R interaction, inducing Ca2+-mediated cell death.
Keywords: Adrenal corticosteroid hormones; Apoptosis; Bcl-2; Calcium (Ca(2+)); Dexamethasone; Endoplasmic reticulum; Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP(3)R); Prednisone.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest, either financially or otherwise. There are not duplicate articles submitted or published elsewhere.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Creating a New Cancer Therapeutic Agent by _targeting the Interaction between Bcl-2 and IP3 Receptors.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Sep 3;11(9):a035196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035196. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 31110129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A synthetic peptide _targeting the BH4 domain of Bcl-2 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma and follicular lymphoma cells alone or in combination with agents _targeting the BH3-binding pocket of Bcl-2.Onco_target. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):27388-402. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.4489. Onco_target. 2015. PMID: 26317541 Free PMC article.
-
A dual role for the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein in cancer: mitochondria versus endoplasmic reticulum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1843(10):2240-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.017. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24768714 Review.
-
Constitutive IP3 signaling underlies the sensitivity of B-cell cancers to the Bcl-2/IP3 receptor disruptor BIRD-2.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Mar;26(3):531-547. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0142-3. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 29899382 Free PMC article.
-
HA14-1 potentiates apoptosis in B-cell cancer cells sensitive to a peptide disrupting IP 3 receptor / Bcl-2 complexes.Int J Dev Biol. 2015;59(7-9):391-8. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.150213gb. Int J Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26260683
Cited by
-
Type 3 Inositol 1,4,5-Trisphosphate Receptor Is Increased and Enhances Malignant Properties in Cholangiocarcinoma.Hepatology. 2020 Feb;71(2):583-599. doi: 10.1002/hep.30839. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 31251815 Free PMC article.
-
Relevance of Membrane Contact Sites in Cancer Progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 12;8:622215. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.622215. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33511135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in uncovering the mechanisms contributing to BIRD-2-induced cell death in B-cell cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Jan 17;10(2):42. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1297-z. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30718472 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of Calcium Signaling in Prostate Cancer Progression: Effects on Cancer Hallmarks and Bone Metastatic Mechanisms.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 25;12(5):1071. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051071. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32344908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creating a New Cancer Therapeutic Agent by _targeting the Interaction between Bcl-2 and IP3 Receptors.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Sep 3;11(9):a035196. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035196. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 31110129 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mikoshiba K, Role of IP3 receptor signaling in cell functions and diseases, Advances in biological regulation, 57 (2015) 217–227. - PubMed
-
- Orrenius S, Gogvadze V, Zhivotovsky B, Calcium and mitochondria in the regulation of cell death, Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 460 (2015) 72–81. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, The Inositol Trisphosphate/Calcium Signaling Pathway in Health and Disease, Physiological reviews, 96 (2016) 1261–1296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

