The Dynamic Roles of TGF-β Signalling in EBV-Associated Cancers
- PMID: 30060514
- PMCID: PMC6115974
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers10080247
The Dynamic Roles of TGF-β Signalling in EBV-Associated Cancers
Abstract
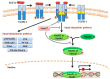
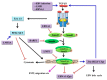
The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signalling pathway plays a critical role in carcinogenesis. It has a biphasic action by initially suppressing tumorigenesis but promoting tumour progression in the later stages of disease. Consequently, the functional outcome of TGF-β signalling is strongly context-dependent and is influenced by various factors including cell, tissue and cancer type. Disruption of this pathway can be caused by various means, including genetic and environmental factors. A number of human viruses have been shown to modulate TGF-β signalling during tumorigenesis. In this review, we describe how this pathway is perturbed in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated cancers and how EBV interferes with TGF-β signal transduction. The role of TGF-β in regulating the EBV life cycle in tumour cells is also discussed.
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma; Epstein-Barr virus; TGF-β signalling; gastric cancer; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The dynamic roles of TGF-β in cancer.J Pathol. 2011 Jan;223(2):205-18. doi: 10.1002/path.2785. Epub 2010 Oct 18. J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 20957627 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) modulates Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in absence of Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with gastric cancer.Cytokine. 2016 Jan;77:176-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.07.023. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 26239415
-
Loss of functional transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta type II receptor results in insensitivity to TGF-beta1-mediated apoptosis and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation.J Med Virol. 2006 Nov;78(11):1456-64. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20719. J Med Virol. 2006. PMID: 16998876
-
Effect of transforming growth factor-beta1 on the cell growth and Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in EBV-infected epithelial cell lines.Virology. 2001 Sep 15;288(1):109-18. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1071. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11543663
-
TGF-β signalling and liver disease.FEBS J. 2016 Jun;283(12):2219-32. doi: 10.1111/febs.13665. Epub 2016 Feb 22. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26807763 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-34c downregulation leads to SOX4 overexpression and cisplatin resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 26;20(1):597. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07081-z. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32586280 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Epstein-Barr virus in gastric cancer: clinicopathological features and prognostic implications.Infect Agent Cancer. 2023 Feb 19;18(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s13027-023-00489-9. Infect Agent Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36803802 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling pathways of EBV-induced oncogenesis.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Feb 6;21(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01793-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 33549103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-genome profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals viral-host co-operation in inflammatory NF-κB activation and immune escape.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 7;12(1):4193. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24348-6. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34234122 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, safety, and correlative biomarkers of bintrafusp alfa in recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal cancer patients: a phase II clinical trial.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023 Sep 6;40:100898. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2023.100898. eCollection 2023 Nov. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2023. PMID: 37701718 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

