Effect of Anlotinib as a Third-Line or Further Treatment on Overall Survival of Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ALTER 0303 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 30098152
- PMCID: PMC6248083
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.3039
Effect of Anlotinib as a Third-Line or Further Treatment on Overall Survival of Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: The ALTER 0303 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial
Erratum in
-
Errors in Number at Risk and Author Email Address.JAMA Oncol. 2018 Nov 1;4(11):1625. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.5345. JAMA Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30419091 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Anlotinib is a novel multi_target tyrosine kinase inhibitor for tumor angiogenesis and proliferative signaling. A phase 2 trial showed anlotinib to improve progression-free survival with a potential benefit of overall survival, leading to the phase 3 trial to confirm the drug's efficacy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Objective: To investigate the efficacy of anlotinib on overall survival of patients with advanced NSCLC progressing after second-line or further treatment.
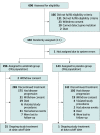
Design, setting, and participants: The ALTER 0303 trial was a multicenter, double-blind, phase 3 randomized clinical trial designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of anlotinib in patients with advanced NSCLC. Patients from 31 grade-A tertiary hospitals in China were enrolled between March 1, 2015, and August 31, 2016. Those aged 18 to 75 years who had histologically or cytologically confirmed NSCLC were eligible (n = 606), and those who had centrally located squamous cell carcinoma with cavitary features or brain metastases that were uncontrolled or controlled for less than 2 months were excluded. Patients (n = 440) were randomly assigned in a 2-to-1 ratio to receive either 12 mg/d of anlotinib or a matched placebo. All cases were treated with study drugs at least once in accordance with the intention-to-treat principle.
Main outcomes and measures: The primary end point was overall survival. The secondary end points were progression-free survival, objective response rate, disease control rate, quality of life, and safety.
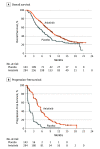
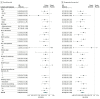
Results: In total, 439 patients were randomized, 296 to the anlotinib group (106 [36.1%] were female and 188 [64.0%] were male, with a mean [SD] age of 57.9 [9.1] years) and 143 to the placebo group (46 [32.2%] were female and 97 [67.8%] were male, with a mean [SD] age of 56.8 [9.1] years). Overall survival was significantly longer in the anlotinib group (median, 9.6 months; 95% CI, 8.2-10.6) than the placebo group (median, 6.3 months; 95% CI, 5.0-8.1), with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.68 (95% CI, 0.54-0.87; P = .002). A substantial increase in progression-free survival was noted in the anlotinib group compared with the placebo group (median, 5.4 months [95% CI, 4.4-5.6] vs 1.4 months [95% CI, 1.1-1.5]; HR, 0.25 [95% CI, 0.19-0.31]; P < .001). Considerable improvement in objective response rate and disease control rate was observed in the anlotinib group over the placebo group. The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events in the anlotinib arm were hypertension and hyponatremia.
Conclusions and relevance: Among the Chinese patients in this trial, anlotinib appears to lead to prolonged overall survival and progression-free survival. This finding suggests that anlotinib is well tolerated and is a potential third-line or further therapy for patients with advanced NSCLC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02388919.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anlotinib as a third-line therapy in patients with refractory advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised phase II trial (ALTER0302).Br J Cancer. 2018 Mar 6;118(5):654-661. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.478. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29438373 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Quality of life results from a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, multi-center phase III trial of anlotinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2018 Aug;122:32-37. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.05.013. Epub 2018 May 18. Lung Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30032842 Clinical Trial.
-
China National Medical Products Administration approval summary: anlotinib for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer after two lines of chemotherapy.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019 Jun 20;39(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0383-7. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31221221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of anlotinib as a third- or further-line therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with different histologic types: Subgroup analysis in the ALTER0303 trial.Cancer Med. 2020 Apr;9(8):2621-2630. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2913. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32064794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anlotinib: First Global Approval.Drugs. 2018 Jul;78(10):1057-1062. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0939-x. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29943374 Review.
Cited by
-
Anlotinib has good efficacy and low toxicity: a phase II study of anlotinib in pre-treated HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2021 Mar 12;18(3):849-59. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0463. Online ahead of print. Cancer Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33710812 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation-based prognostic scoring system for predicting the prognosis of advanced small cell lung cancer patients receiving anlotinib monotherapy.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Dec;36(12):e24772. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24772. Epub 2022 Nov 28. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 36441595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Case report: Unique FLT4 variants associated with differential response to anlotinib in angiosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 14;12:1027696. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1027696. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36452496 Free PMC article.
-
QALY-type preference and willingness-to-pay among end-of-life patients with cancer treatments: a pilot study using discrete choice experiment.Qual Life Res. 2024 Mar;33(3):753-765. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03562-3. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Qual Life Res. 2024. PMID: 38079024
-
Efficacy of Immunotherapy Combined with Antiangiogenic Therapy in Treatment-Failure Patients with Advanced Carcinoma Ex Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Submandibular Gland: A Case Report.Curr Oncol. 2022 Sep 1;29(9):6334-6341. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29090498. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36135067 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

