Bradykinin B2 Receptor Contributes to Inflammatory Responses in Human Endothelial Cells by the Transactivation of the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor FGFR-1
- PMID: 30200598
- PMCID: PMC6163484
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19092638
Bradykinin B2 Receptor Contributes to Inflammatory Responses in Human Endothelial Cells by the Transactivation of the Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor FGFR-1
Abstract
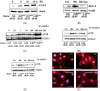
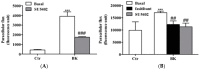
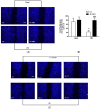
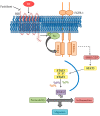
Elevated levels of bradykinin (BK) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and angiogenic disorders. In angiogenesis, both stimuli induce a pro-inflammatory signature in endothelial cells, activating an autocrine/paracrine amplification loop that sustains the neovascularization process. Here we investigated the contribution of the FGF-2 pathway in the BK-mediated human endothelial cell permeability and migration, and the role of the B2 receptor (B2R) of BK in this cross-talk. BK (1 µM) upregulated the FGF-2 expression and promoted the FGF-2 signaling, both in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and in retinal capillary endothelial cells (HREC) by the activation of Fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR-1) and its downstream signaling (fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate: FRSα, extracellular signal⁻regulated kinases1/2: ERK1/2, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3: STAT3 phosphorylation). FGFR-1 phosphorylation triggered by BK was c-Src mediated and independent from FGF-2 upregulation. Either HUVEC and HREC exposed to BK showed increased permeability, disassembly of adherens and tight-junction, and increased cell migration. B2R blockade by the selective antagonist, fasitibant, significantly inhibited FGF-2/FGFR-1 signaling, and in turn, BK-mediated endothelial cell permeability and migration. Similarly, the FGFR-1 inhibitor, SU5402, and the knock-down of the receptor prevented the BK/B2R inflammatory response in endothelial cells. In conclusion, this work demonstrates the existence of a BK/B2R/FGFR-1/FGF-2 axis in endothelial cells that might be implicated in propagation of angiogenic/inflammatory responses. A B2R blockade, by abolishing the initial BK stimulus, strongly attenuated FGFR-1-driven cell permeability and migration.
Keywords: B2R antagonist; FGFR-1; bradykinin; endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


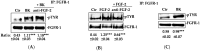




Similar articles
-
Antagonism of bradykinin B2 receptor prevents inflammatory responses in human endothelial cells by quenching the NF-kB pathway activation.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 2;9(1):e84358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084358. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24392129 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Bradykinin B2 Receptor in Pathological Vascularization in Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in Mice and Rabbit Cornea.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 23;19(2):330. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020330. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29360776 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 regulates angiogenesis via activation of fibroblast growth factor receptor-1.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 25;283(4):2139-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703090200. Epub 2007 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18042549
-
The potential of fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling as a therapeutic _target in tumor angiogenesis.Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2015;19(10):1361-77. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1062475. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Expert Opin Ther _targets. 2015. PMID: 26125971 Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Skin Cancers.Cells. 2019 Jun 4;8(6):540. doi: 10.3390/cells8060540. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31167513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The antiplatelet agent revacept prevents the increase of systemic thromboxane A2 biosynthesis and neointima hyperplasia.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 8;10(1):21420. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77934-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33293599 Free PMC article.
-
Formyl-peptide receptor 2 signalling triggers aerobic metabolism of glucose through Nox2-dependent modulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase activity.Open Biol. 2023 Oct;13(10):230336. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230336. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Open Biol. 2023. PMID: 37875162 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of FGFR gene polymorphisms on response and toxicity of cyclophosphamide-epirubicin-docetaxel-based chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2018 Oct 25;18(1):1038. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4951-z. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30359238 Free PMC article.
-
The Outcome of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients Is Linked to Thromboinflammation Dominated by the Kallikrein/Kinin System.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 22;12:627579. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.627579. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33692801 Free PMC article.
-
How the Innate Immune System of the Blood Contributes to Systemic Pathology in COVID-19-Induced ARDS and Provides Potential _targets for Treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 8;13:840137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840137. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35350780 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cervenak L., Morbidelli L., Donati D., Donnini S., Kambayashi T., Wilson J.L., Axelson H., Castaños-Velez E., Ljunggren H.G., Malefyt R.D., et al. Abolished angiogenicity and tumorigenicity of burkitt lymphoma by interleukin-10. Blood. 2000;96:2568–2573. - PubMed
-
- Presta M., Andrés G., Leali D., Dell’Era P., Ronca R. Inflammatory cells and chemokines sustain fgf2-induced angiogenesis. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2009;20:39–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

