Ferroptosis and Its Role in Diverse Brain Diseases
- PMID: 30406908
- PMCID: PMC6506411
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-018-1403-3
Ferroptosis and Its Role in Diverse Brain Diseases
Abstract
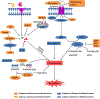
Ferroptosis is a recently identified, iron-regulated, non-apoptotic form of cell death. It is characterized by cellular accumulation of lipid reactive oxygen species that ultimately leads to oxidative stress and cell death. Although first identified in cancer cells, ferroptosis has been shown to have significant implications in several neurologic diseases, such as ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease. This review summarizes current research on ferroptosis, its underlying mechanisms, and its role in the progression of different neurologic diseases. Understanding the role of ferroptosis could provide valuable information regarding treatment and prevention of these devastating diseases.
Keywords: Brain disease; Cancer; Ferroptosis; Stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases.Neurosci Lett. 2021 Mar 16;747:135614. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135614. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33485988 Review.
-
Ferroptosis and its potential role in the physiopathology of Parkinson's Disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2021 Jan;196:101890. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101890. Epub 2020 Jul 26. Prog Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 32726602 Review.
-
Ferroptosis: mechanisms and links with diseases.Signal Transduct _target Ther. 2021 Feb 3;6(1):49. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00428-9. Signal Transduct _target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33536413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis: A potential therapeutic _target for neurodegenerative diseases.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021 Aug;35(8):e22830. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22830. Epub 2021 May 28. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34047408 Review.
-
Ferroptosis Mechanisms Involved in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 20;21(22):8765. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228765. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal exposure to nanopolystyrene induces neurotoxicity in offspring through P53-mediated ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in the rat hippocampus.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 23;22(1):651. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02911-9. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39438901 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles induced ferroptosis via Beclin1/ATG5-dependent autophagy pathway.Nano Converg. 2021 Apr 2;8(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40580-021-00260-z. Nano Converg. 2021. PMID: 33796911 Free PMC article.
-
Blood transcriptome analysis: Ferroptosis and potential inflammatory pathways in post-traumatic stress disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 5;13:841999. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.841999. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36276334 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin Protects against MPP+/MPTP-Induced Dopaminergic Neuron Death in Parkinson's Disease by Inhibiting Ferroptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 5;2022:7769355. doi: 10.1155/2022/7769355. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36105483 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying potential therapeutic _targets for ischemic stroke through immune infiltration analysis and construction of a programmed cell death‑related ceRNA network.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Sep 21;24(5):680. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11616. eCollection 2022 Nov. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36185765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji AF, Clish CB, Brown LM, Girotti AW, Cornish VW, Schreiber SL, Stockwell BR (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156 (1–2):317–331. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

