Effect of Linagliptin vs Placebo on Major Cardiovascular Events in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular and Renal Risk: The CARMELINA Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 30418475
- PMCID: PMC6583576
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.18269
Effect of Linagliptin vs Placebo on Major Cardiovascular Events in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and High Cardiovascular and Renal Risk: The CARMELINA Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Type 2 diabetes is associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk. Prior trials have demonstrated CV safety of 3 dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors but have included limited numbers of patients with high CV risk and chronic kidney disease.
Objective: To evaluate the effect of linagliptin, a selective DPP-4 inhibitor, on CV outcomes and kidney outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes at high risk of CV and kidney events.
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter noninferiority trial conducted from August 2013 to August 2016 at 605 clinic sites in 27 countries among adults with type 2 diabetes, hemoglobin A1c of 6.5% to 10.0%, high CV risk (history of vascular disease and urine-albumin creatinine ratio [UACR] >200 mg/g), and high renal risk (reduced eGFR and micro- or macroalbuminuria). Participants with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) were excluded. Final follow-up occurred on January 18, 2018.
Interventions: Patients were randomized to receive linagliptin, 5 mg once daily (n = 3494), or placebo once daily (n = 3485) added to usual care. Other glucose-lowering medications or insulin could be added based on clinical need and local clinical guidelines.
Main outcomes and measures: Primary outcome was time to first occurrence of the composite of CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke. Criteria for noninferiority of linagliptin vs placebo was defined by the upper limit of the 2-sided 95% CI for the hazard ratio (HR) of linagliptin relative to placebo being less than 1.3. Secondary outcome was time to first occurrence of adjudicated death due to renal failure, ESRD, or sustained 40% or higher decrease in eGFR from baseline.
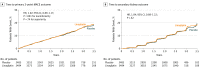
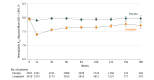
Results: Of 6991 enrollees, 6979 (mean age, 65.9 years; eGFR, 54.6 mL/min/1.73 m2; 80.1% with UACR >30 mg/g) received at least 1 dose of study medication and 98.7% completed the study. During a median follow-up of 2.2 years, the primary outcome occurred in 434 of 3494 (12.4%) and 420 of 3485 (12.1%) in the linagliptin and placebo groups, respectively, (absolute incidence rate difference, 0.13 [95% CI, -0.63 to 0.90] per 100 person-years) (HR, 1.02; 95% CI, 0.89-1.17; P < .001 for noninferiority). The kidney outcome occurred in 327 of 3494 (9.4%) and 306 of 3485 (8.8%), respectively (absolute incidence rate difference, 0.22 [95% CI, -0.52 to 0.97] per 100 person-years) (HR, 1.04; 95% CI, 0.89-1.22; P = .62). Adverse events occurred in 2697 (77.2%) and 2723 (78.1%) patients in the linagliptin and placebo groups; 1036 (29.7%) and 1024 (29.4%) had 1 or more episodes of hypoglycemia; and there were 9 (0.3%) vs 5 (0.1%) events of adjudication-confirmed acute pancreatitis.
Conclusions and relevance: Among adults with type 2 diabetes and high CV and renal risk, linagliptin added to usual care compared with placebo added to usual care resulted in a noninferior risk of a composite CV outcome over a median 2.2 years.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01897532.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the CArdiovascular safety and Renal Microvascular outcomE study with LINAgliptin (CARMELINA®): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardio-renal risk.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Mar 14;17(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0682-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 29540217 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hypoglycemia and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the CARMELINA and CAROLINA Trials of Linagliptin: A Secondary Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials.JAMA Cardiol. 2024 Feb 1;9(2):134-143. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2023.4602. JAMA Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38170502 Free PMC article.
-
Linagliptin Effects on Heart Failure and Related Outcomes in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at High Cardiovascular and Renal Risk in CARMELINA.Circulation. 2019 Jan 15;139(3):351-361. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038352. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 30586723 Clinical Trial.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and cardiovascular and renal disease in type 2 diabetes: What have we learned from the CARMELINA trial?Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019 Jul;16(4):303-309. doi: 10.1177/1479164119842339. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019. PMID: 31018682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease or risk factors.Postgrad Med. 2015;127(8):842-54. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2015.1095616. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Postgrad Med. 2015. PMID: 26436470 Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights into the Pleiotropic Actions of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Beyond Glycaemic Control.touchREV Endocrinol. 2024 Oct;20(2):19-29. doi: 10.17925/EE.2024.20.2.5. Epub 2024 Sep 6. touchREV Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39526061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diabetes cardiovascular outcomes trials and racial and ethnic minority enrollment: impact, barriers, and potential solutions.Front Public Health. 2024 Oct 25;12:1412874. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1412874. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39525461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease prevention in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with multiple network meta-regressions.World J Diabetes. 2024 Oct 15;15(10):2135-2146. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i10.2135. World J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39493569 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and cardiovascular events among patients with type 2 diabetes and low-to-normal body mass index: a nationwide cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Oct 22;23(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02478-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39438867 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin Use Is Associated With Lower Risk of All-Cause Mortality, Hospitalization for Heart Failure, and End-Stage Renal Disease Compared to DPP-4i in Nordic Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Results From the EMPRISE (Empagliflozin Comparative Effectiveness and Safety) Study.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Oct 12;2024:6142211. doi: 10.1155/2024/6142211. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39430801 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

