GALAD Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Detection in Comparison with Liver Ultrasound and Proposal of GALADUS Score
- PMID: 30464023
- PMCID: PMC6401221
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-18-0281
GALAD Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Detection in Comparison with Liver Ultrasound and Proposal of GALADUS Score
Abstract
Background: The GALAD score is a serum biomarker-based model that predicts the probability of having hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with chronic liver disease. We aimed to assess the performance of the GALAD score in comparison with liver ultrasound for detection of HCC.
Methods: A single-center cohort of 111 HCC patients and 180 controls with cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis B and a multicenter cohort of 233 early HCC and 412 cirrhosis patients from the Early Detection Research Network (EDRN) phase II HCC Study were analyzed.
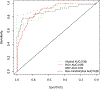
Results: The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the GALAD score for HCC detection was 0.95 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.93-97], which was higher than the AUC of ultrasound (0.82, P <0.01). At a cutoff of -0.76, the GALAD score had a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 85% for HCC detection. The AUC of the GALAD score for early-stage HCC detection remained high at 0.92 (95% CI, 0.88-0.96; cutoff -1.18, sensitivity 92%, specificity 79%). The AUC of the GALAD score for HCC detection was 0.88 (95% CI, 0.85-0.91) in the EDRN cohort. The combination of GALAD and ultrasound (GALADUS score) further improved the performance of the GALAD score in the single-center cohort, achieving an AUC of 0.98 (95% CI, 0.96-0.99; cutoff -0.18, sensitivity 95%, specificity 91%).
Conclusions: The performance of the GALAD score was superior to ultrasound for HCC detection. The GALADUS score further enhanced the performance of the GALAD score.
Impact: The GALAD score was validated in the United States.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest:
LRR has received grant funding from BTG, Gilead Sciences and Wako Diagnostics; HY is an employee of Wako Diagnostics. No other potential conflict of interest for the rest of authors.
Figures
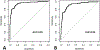
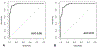
Similar articles
-
GALAD score and a proposal for GALADUS model for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in Vietnamese patients with chronic liver disease.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Feb;28(3):1111-1122. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202402_35348. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38375717
-
GALAD Score Detects Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma in an International Cohort of Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar;18(3):728-735.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.11.012. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31712073
-
Diagnostic and prognostic performances of GALAD score in staging and 1-year mortality of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 May 7;30(17):2343-2353. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i17.2343. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38813057 Free PMC article.
-
The Performance of GALAD Score for Diagnosing Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 26;12(3):949. doi: 10.3390/jcm12030949. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance: An evidence-based approach.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Apr 7;25(13):1550-1559. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i13.1550. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30983815 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in treated and untreated patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Jul;29(3):605-622. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0342. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36788759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review article: Available modalities for screening and imaging diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma-Current gaps and challenges.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023 May;57(10):1056-1065. doi: 10.1111/apt.17506. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37038283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GALAD score as a prognostic model for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after local ablation.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 May 7;150(5):241. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05760-z. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38713414 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor DNA and Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Semin Liver Dis. 2019 Nov;39(4):452-462. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688503. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Semin Liver Dis. 2019. PMID: 31226727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chinese expert consensus statement on the clinical application of AFP/AFP-L3%/DCP using GALAD and GALAD-like algorithm in HCC.J Clin Lab Anal. 2023 Dec;37(23-24):e24990. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24990. Epub 2023 Dec 8. J Clin Lab Anal. 2023. PMID: 38063322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA oncology 2017;3(4):524–48 doi 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

