Cancellation of Bessel beam side lobes for high-contrast light sheet microscopy
- PMID: 30464219
- PMCID: PMC6249239
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-35006-1
Cancellation of Bessel beam side lobes for high-contrast light sheet microscopy
Abstract
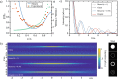
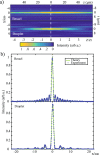
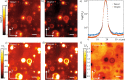
An ideal illumination for light sheet fluorescence microscopy entails both a localized and a propagation invariant optical field. Bessel beams and Airy beams satisfy these conditions, but their non-diffracting feature comes at the cost of the presence of high-energy side lobes that notably degrade the imaging contrast and induce photobleaching. Here, we demonstrate the use of a light droplet illumination whose side lobes are suppressed by interfering Bessel beams of specific k-vectors. Our droplet illumination readily achieves more than 50% extinction of the light distributed across the Bessel side lobes, providing a more efficient energy localization without loss in transverse resolution. In a standard light sheet fluorescence microscope, we demonstrate a two-fold contrast enhancement imaging micron-scale fluorescent beads. Results pave the way to new opportunities for rapid and deep in vivo observations of large-scale biological systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A compact Airy beam light sheet microscope with a tilted cylindrical lens.Biomed Opt Express. 2014 Sep 5;5(10):3434-42. doi: 10.1364/BOE.5.003434. eCollection 2014 Oct 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2014. PMID: 25360362 Free PMC article.
-
Improving axial resolution of Bessel beam light-sheet fluorescence microscopy by photobleaching imprinting.Opt Express. 2020 Mar 30;28(7):9464-9476. doi: 10.1364/OE.388808. Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 32225553
-
Axial resolution enhancement of light-sheet microscopy by double scanning of Bessel beam and its complementary beam.J Biophotonics. 2019 Jan;12(1):e201800094. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201800094. Epub 2018 Aug 20. J Biophotonics. 2019. PMID: 30043551
-
Bessel Beams in Ophthalmology: A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Aug 27;14(9):1672. doi: 10.3390/mi14091672. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light sheet fluorescence microscopy for neuroscience.J Neurosci Methods. 2019 May 1;319:16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.07.011. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Neurosci Methods. 2019. PMID: 30048674 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering a better light sheet in an axicon-based system using a flattened Gaussian beam of low order.J Biophotonics. 2022 Jun;15(6):e202100342. doi: 10.1002/jbio.202100342. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Biophotonics. 2022. PMID: 35104051 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput volumetric mapping of synaptic transmission.Nat Methods. 2024 Jul;21(7):1298-1305. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02309-3. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Nat Methods. 2024. PMID: 38898094
-
Incoherent superposition of polychromatic light enables single-shot nondiffracting light-sheet microscopy.Opt Express. 2021 Sep 27;29(20):32691-32699. doi: 10.1364/OE.439338. Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 34615334 Free PMC article.
-
Minutes-timescale 3D isotropic imaging of entire organs at subcellular resolution by content-aware compressed-sensing light-sheet microscopy.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 4;12(1):107. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20329-3. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33398061 Free PMC article.
-
Scattering Assisted Imaging.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 14;9(1):4591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40997-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30872736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Olarte OE, Andilla J, Gualda EJ, Loza-Alvarez P. Light-sheet microscopy: a tutorial. Adv. Opt. Phot. 2018;10:111–179.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

