Isoquercetin Improves Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Activating AMPK Pathway and Suppressing TGF-β Signaling on an HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rat Model
- PMID: 30572631
- PMCID: PMC6321444
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19124126
Isoquercetin Improves Hepatic Lipid Accumulation by Activating AMPK Pathway and Suppressing TGF-β Signaling on an HFD-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Rat Model
Abstract
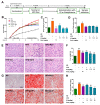
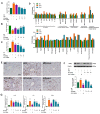
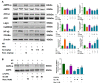
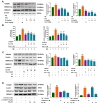
Isoquercetin (IQ), a glucoside derivative of quercetin, has been reported to have beneficial effects in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, we investigated the potential improvement of IQ in liver lipid accumulation, inflammation, oxidative condition, and activation in Kupffer cells (KCs) on a high-fat diet (HFD) induced NAFLD models. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were induced by HFD, lipopolysaccharides/free fatty acids (LPS/FFA) induced co-culture cells model between primary hepatocytes and Kupffer cells was used to test the effects and the underlying mechanism of IQ. Molecular docking was performed to predict the potential _target of IQ. Significant effects of IQ were found on reduced lipid accumulation, inflammation, and oxidative stress. In addition, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway was activated by IQ, and is plays an important role in lipid regulation. Meanwhile, IQ reversed the increase of activated KCs which caused by lipid overload, and also suppression of Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling by TGF-β Recptor-1 and SMAD2/3 signaling. Finally, TGF-βR1 and TGF-βR2 were both found may involve in the mechanism of IQ. IQ can improve hepatic lipid accumulation and decrease inflammation and oxidative stress by its activating AMPK pathway and suppressing TGF-β signaling to alleviate NAFLD.
Keywords: AMPK; Kupffer cell; NAFLD; TGF-β; isoquercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liensinine alleviates high fat diet (HFD)-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via regulating TAK1/AMPK signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Mar;104:108306. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108306. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34999396
-
Allyl isothiocyanate ameliorates lipid accumulation and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the Sirt1/AMPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Sep 14;25(34):5120-5133. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i34.5120. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31558861 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced oxidative stress contributes to the lipid lowering effects of isoquercitrin in free fatty acids induced hepatocytes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:313602. doi: 10.1155/2014/313602. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014. PMID: 25404990 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic AMP Kinase as a Potential _target for Treating Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Evidence from Studies of Natural Products.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(8):889-907. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170404142450. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28393690 Review.
-
Kupffer cells: increasingly significant role in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Ann Hepatol. 2014 Sep-Oct;13(5):489-95. Ann Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 25152980 Review.
Cited by
-
Communication in non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and role of immunomodulatory nutraceuticals in their management.Front Nutr. 2022 Sep 21;9:966152. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.966152. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36211513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and validation of potential diagnostic signature and immune cell infiltration for NAFLD based on cuproptosis-related genes by bioinformatics analysis and machine learning.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 26;14:1251750. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1251750. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37822923 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Diseases: Nutraceutical Interventions Related to Caloric Restriction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 21;22(15):7772. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157772. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of Kupffer cells in NAFLD and NASH: mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 16;11:1199519. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1199519. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37261074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoquercitrin Attenuates Steatohepatitis by Inhibition of the Activated NLRP3 Inflammasome through HSP90.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8795. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108795. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240141 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballestri S., Nascimbeni F., Baldelli E., Marrazzo A., Romagnoli D., Lonardo A. NAFLD as a Sexual Dimorphic Disease: Role of Gender and Reproductive Status in the Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Inherent Cardiovascular Risk. Adv. Ther. 2017;34:1291–1326. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0556-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

