Neuronal Regulation of Fast Synaptotagmin Isoforms Controls the Relative Contributions of Synchronous and Asynchronous Release
- PMID: 30733150
- PMCID: PMC6788794
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.01.013
Neuronal Regulation of Fast Synaptotagmin Isoforms Controls the Relative Contributions of Synchronous and Asynchronous Release
Abstract
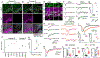
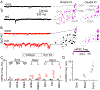
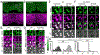
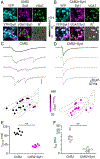
Neurotransmitter release can be synchronous and occur within milliseconds of action potential invasion, or asynchronous and persist for tens of milliseconds. The molecular determinants of release kinetics remain poorly understood. It has been hypothesized that asynchronous release dominates when fast Synaptotagmin isoforms are far from calcium channels or when specialized sensors, such as Synaptotagmin 7, are abundant. Here we test these hypotheses for GABAergic projections onto neurons of the inferior olive, where release in different subnuclei ranges from synchronous to asynchronous. Surprisingly, neither of the leading hypotheses accounts for release kinetics. Instead, we find that rapid Synaptotagmin isoforms are abundant in subnuclei with synchronous release but absent where release is asynchronous. Viral expression of Synaptotagmin 1 transforms asynchronous synapses into synchronous ones. Thus, the nervous system controls levels of fast Synaptotagmin isoforms to regulate release kinetics and thereby controls the ability of synapses to encode spike rates or precise timing.
Keywords: Syt7; asynchronous release; cerebellum; inferior olive; short-term plasticity; synaptotagmin.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synaptotagmin-7 Is Essential for Ca2+-Triggered Delayed Asynchronous Release But Not for Ca2+-Dependent Vesicle Priming in Retinal Ribbon Synapses.J Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;35(31):11024-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0759-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26245964 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin 7 Mediates Both Facilitation and Asynchronous Release at Granule Cell Synapses.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 28;38(13):3240-3251. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3207-17.2018. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29593071 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar and vestibular nuclear synapses in the inferior olive have distinct release kinetics and neurotransmitters.Elife. 2020 Dec 1;9:e61672. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61672. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33259288 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic control of neurotransmitter release by different members of the synaptotagmin family.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Aug;51:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.05.006. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29886350 Review.
-
The diversity of synaptotagmin isoforms.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2020 Aug;63:198-209. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2020.04.006. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32663762 Review.
Cited by
-
Synaptotagmin-1 enables frequency coding by suppressing asynchronous release in a temperature dependent manner.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 5;9(1):11341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47487-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31383906 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Synaptotagmin 7 negatively regulates synaptic vesicle release and replenishment in a dosage-dependent manner.Elife. 2020 Apr 28;9:e55443. doi: 10.7554/eLife.55443. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32343229 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmins 3 and 7 mediate the majority of asynchronous release from synapses in the cerebellum and hippocampus.Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 27;43(8):114595. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114595. Epub 2024 Aug 6. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39116209 Free PMC article.
-
Complexin has a dual synaptic function as checkpoint protein in vesicle priming and as a promoter of vesicle fusion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 9;121(15):e2320505121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2320505121. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38568977 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptotagmin 7 docks synaptic vesicles to support facilitation and Doc2α-triggered asynchronous release.Elife. 2024 Mar 27;12:RP90632. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90632. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38536730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ABBOTT LF & REGEHR WG 2004. Synaptic computation. Nature, 431, 796–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

