Maternal-biased H3K27me3 correlates with paternal-specific gene expression in the human morula
- PMID: 30808660
- PMCID: PMC6446541
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.323105.118
Maternal-biased H3K27me3 correlates with paternal-specific gene expression in the human morula
Abstract
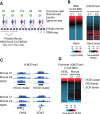
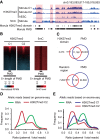
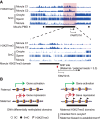
Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic mechanism by which genes are expressed in a parental origin-dependent manner. We recently discovered that, like DNA methylation, oocyte-inherited H3K27me3 can also serve as an imprinting mark in mouse preimplantation embryos. In this study, we found H3K27me3 is strongly biased toward the maternal allele with some associated with DNA methylation-independent paternally expressed genes (PEGs) in human morulae. The H3K27me3 domains largely overlap with DNA partially methylated domains (PMDs) and occupy developmental gene promoters. Thus, our study not only reveals the H3K27me3 landscape but also establishes a correlation between maternal-biased H3K27me3 and PEGs in human morulae.
Keywords: DNA methylation; allele-specific gene expression; genomic imprinting; human morulae; maternal-biased H3K27me3.
© 2019 Zhang et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Allelic H3K27me3 to allelic DNA methylation switch maintains noncanonical imprinting in extraembryonic cells.Sci Adv. 2019 Dec 20;5(12):eaay7246. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay7246. eCollection 2019 Dec. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 32064321 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal H3K27me3 controls DNA methylation-independent imprinting.Nature. 2017 Jul 27;547(7664):419-424. doi: 10.1038/nature23262. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28723896 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide high resolution parental-specific DNA and histone methylation maps uncover patterns of imprinting regulation in maize.Genome Res. 2014 Jan;24(1):167-76. doi: 10.1101/gr.155879.113. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24131563 Free PMC article.
-
There is another: H3K27me3-mediated genomic imprinting.Trends Genet. 2022 Jan;38(1):82-96. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.06.017. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Trends Genet. 2022. PMID: 34304914 Review.
-
Maternal H3K27me3-dependent autosomal and X chromosome imprinting.Nat Rev Genet. 2020 Sep;21(9):555-571. doi: 10.1038/s41576-020-0245-9. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Nat Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32514155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Creation of true interspecies hybrids: Rescue of hybrid class with hybrid cytoplasm affecting growth and metabolism.Sci Adv. 2024 Oct 25;10(43):eadq4339. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adq4339. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 39441922 Free PMC article.
-
Features and mechanisms of canonical and noncanonical genomic imprinting.Genes Dev. 2021 Jun;35(11-12):821-834. doi: 10.1101/gad.348422.121. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 34074696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conservation and divergence of canonical and non-canonical imprinting in murids.Genome Biol. 2023 Mar 14;24(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02869-1. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 36918927 Free PMC article.
-
Allelic H3K27me3 to allelic DNA methylation switch maintains noncanonical imprinting in extraembryonic cells.Sci Adv. 2019 Dec 20;5(12):eaay7246. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aay7246. eCollection 2019 Dec. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 32064321 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide profiling of histone H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 modifications in individual blastocysts by CUT&Tag without a solid support (NON-TiE-UP CUT&Tag).Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 11;12(1):11727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15417-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35821505 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
