Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: knowns and unknowns
- PMID: 30814139
- PMCID: PMC9489101
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0100-2018
Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: knowns and unknowns
Abstract
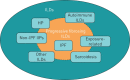
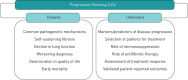
Patients with certain types of fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD) are at risk of developing a progressive phenotype characterised by self-sustaining fibrosis, decline in lung function, worsening quality of life, and early mortality. It has been proposed that such progressive fibrosing ILDs, which show commonalities in clinical behaviour and in the pathogenetic mechanisms that drive progressive fibrosis, may be "lumped" together for the purposes of clinical research and, potentially, for treatment. At present, no drugs are approved for the treatment of ILDs other than nintedanib and pirfenidone for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. For other progressive fibrosing ILDs, the mainstay of drug therapy is immunosuppression. However, it is postulated that, once the response to lung injury in fibrosing ILDs has reached the stage at which fibrosis has become progressive and self-sustaining, _targeted antifibrotic therapy would be required to slow disease progression. Nintedanib, an intracellular inhibitor of tyrosine kinases, has shown antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory and vascular remodelling effects in several non-clinical models of fibrosis, irrespective of the trigger for the injury. Ongoing clinical trials will provide insight into the role of antifibrotic treatment with nintedanib or pirfenidone in the management of fibrosing ILDs with a progressive phenotype.
Copyright ©ERS 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: V. Cottin reports personal fees from Actelion (for consultancy, lectures and travel to medical meetings), Boehringer Ingelheim (for development of educational presentations, consultancy, lectures and travel to medical meetings), Bayer (for consultancy), Gilead (as a member of an adjudication committee), MSD (for consultancy and travel to medical meetings), Novartis (for consultancy and lectures), Roche (for consultancy, lectures and travel to medical meetings), Sanofi (for consultancy and lectures), Promedior (as chair of the Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB)), Celgene (for the DSMB) and Galapagos (for consultancy and as chair of the DSMB), as well as grants from Boehringer Ingelheim and Roche to his institution, all outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: L. Wollin is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Conflict of interest: A. Fischer reports grants and consultancy fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, and consultancy fees from F. Hoffman La Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer and Genentech, during the conduct of the study. Conflict of interest: M. Quaresma is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Conflict of interest: S. Stowasser is an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Conflict of interest: S. Harari reports grants and personal fees from Roche, Actelion and Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. In addition to being investigator in trials involving these companies, relationships include lectures and membership of scientific advisory boards, and grants for research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Possible value of antifibrotic drugs in patients with progressive fibrosing non-IPF interstitial lung diseases.BMC Pulm Med. 2019 Nov 12;19(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-0937-0. BMC Pulm Med. 2019. PMID: 31718637 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological management of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: a review of the current evidence.Eur Respir Rev. 2018 Dec 21;27(150):180074. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0074-2018. Print 2018 Dec 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2018. PMID: 30578333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases.Eur Respir J. 2019 Sep 19;54(3):1900161. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00161-2019. Print 2019 Sep. Eur Respir J. 2019. PMID: 31285305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nintedanib: A Review in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases.Drugs. 2021 Apr;81(5):575-586. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01487-0. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33765296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: A new concept and indication of nintedanib.Mod Rheumatol. 2021 Jan;31(1):13-19. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2020.1826665. Mod Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 32964766 Review.
Cited by
-
The burden of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial lung diseases: a systematic evidence synthesis.Respir Res. 2024 Aug 27;25(1):325. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-02897-w. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39192278 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic and immune-related pulmonary fibrosis: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges.Clin Transl Immunology. 2019 Nov 5;8(11):e1086. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1086. eCollection 2019. Clin Transl Immunology. 2019. PMID: 31709050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: a milestone in the management of interstitial lung diseases.Eur Respir Rev. 2019 Oct 1;28(153):190109. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0109-2019. Print 2019 Sep 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2019. PMID: 31578213 Free PMC article.
-
The role of antifibrotics in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2022 Feb 15;14:1759720X221074457. doi: 10.1177/1759720X221074457. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2022. PMID: 35186127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitivity of transbronchial lung cryobiopsy in the diagnosis of different interstitial lung diseases.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):22037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26510-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36543857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belloli EA, Beckford R, Hadley R, et al. . Idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Respirology 2016; 21: 259–268. - PubMed
-
- Hyldgaard C, Bendstrup E, Wells AU, et al. . Unclassifiable interstitial lung diseases: clinical characteristics and survival. Respirology 2017; 22: 494–500. - PubMed
-
- Fischer A, Chartrand S. Assessment and management of connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 2015; 32: 2–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
