Transcriptome and Proteome-Based Network Analysis Reveals a Model of Gene Activation in Wheat Resistance to Stripe Rust
- PMID: 30836695
- PMCID: PMC6429138
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20051106
Transcriptome and Proteome-Based Network Analysis Reveals a Model of Gene Activation in Wheat Resistance to Stripe Rust
Abstract
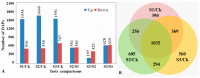
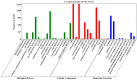
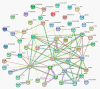
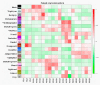
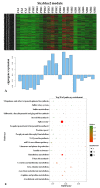
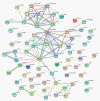
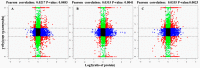
Stripe rust, caused by the pathogen Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst), is an important fungal foliar disease of wheat (Triticum aestivum). To study the mechanism underlying the defense of wheat to Pst, we used the next-generation sequencing and isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) technologies to generate transcriptomic and proteomic profiles of seedling leaves at different stages under conditions of pathogen stress. By conducting comparative proteomic analysis using iTRAQ, we identified 2050, 2190, and 2258 differentially accumulated protein species at 24, 48, and 72 h post-inoculation (hpi). Using pairwise comparisons and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) of the transcriptome, we identified a stress stage-specific module enriching in transcription regulator genes. The homologs of several regulators, including splicing and transcription factors, were similarly identified as hub genes operating in the Pst-induced response network. Moreover, the Hsp70 protein were predicted as a key point in protein⁻protein interaction (PPI) networks from STRING database. Taking the genetics resistance gene locus into consideration, we identified 32 induced proteins in chromosome 1BS as potential candidates involved in Pst resistance. This study indicated that the transcriptional regulation model plays an important role in activating resistance-related genes in wheat responding to Pst stress.
Keywords: WGCNA; iTRAQ; splicing regulator; stripe rust; transcriptome-proteome associated analysis; wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the mechanisms underlying wheat cultivar Shumai126 responding to stripe rust.Gene. 2021 Feb 5;768:145290. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145290. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33157204
-
Comparative transcriptomic insights into molecular mechanisms of the susceptibility wheat variety MX169 response to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst) infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):e0377423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03774-23. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38916358 Free PMC article.
-
Monodehydroascorbate reductase gene, regulated by the wheat PN-2013 miRNA, contributes to adult wheat plant resistance to stripe rust through ROS metabolism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1839(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.11.001. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24269602
-
Epigenetics of wheat-rust interaction: an update.Planta. 2022 Jan 27;255(2):50. doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-03829-y. Planta. 2022. PMID: 35084577 Review.
-
Omics Approaches for the Engineering of Pathogen Resistant Plants.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2016;19:89-98. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26363625 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomics and co-expression network analysis revealing candidate genes for the laccase activity of Trametes gibbosa.BMC Microbiol. 2023 Jan 26;23(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02727-3. BMC Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36703110 Free PMC article.
-
Wheat Omics: Advancements and Opportunities.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 17;12(3):426. doi: 10.3390/plants12030426. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Association Mapping of Crown and Brown Rust Resistance in Perennial Ryegrass.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 22;13(1):20. doi: 10.3390/genes13010020. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052360 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for iron and zinc bio-fortification in genetically diverse germplasm of maize (Zea mays L): A systematic review.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 24;8(12):e12593. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12593. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36619433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals the molecular mechanisms of response to an emergent yellow-flower disease in green Chinese prickly ash (Zanthoxylum schinifolium).Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 23;11(1):18886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98427-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34556742 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McIntosh R., Yamazaki Y., Dubcovsky J., Rogers J., Morris C., Appels R., Xia X. Catalogue of gene symbols for wheat 2013–2014 supplement; Proceedings of the 12th International Wheat Genetic Symposium; Yokohama, Japan. 8–13 September 2013.
-
- Zhang H., Zhang L., Wang C., Wang Y., Zhou X., Lv S., Liu X., Kang Z., Ji W. Molecular mapping and marker development for the Triticum dicoccoides-derived stripe rust resistance gene YrSM139-1B in bread wheat cv. Shaanmai 139. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016;129:369–376. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2633-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

