RIPK1 can mediate apoptosis in addition to necroptosis during embryonic development
- PMID: 30867408
- PMCID: PMC6416317
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1490-8
RIPK1 can mediate apoptosis in addition to necroptosis during embryonic development
Abstract
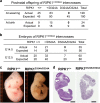
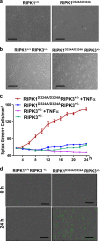
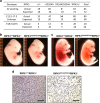
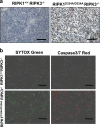
RIPK1 has emerged as a key effector in programmed necrosis or necroptosis. This function of RIPK1 is mediated by its protein serine/threonine kinase activity and through the downstream kinase RIPK3. Deletion of RIPK1 prevents embryonic lethality in mice lacking FADD, a signaling adaptor protein required for activation of Caspase 8 in extrinsic apoptotic pathways. This indicates that FADD-mediated apoptosis inhibits RIPK1-dependent necroptosis to ensure successful embryogenesis. However, the molecular mechanism for this critical regulation remains unclear. In the current study, a novel mouse model has been generated, by disrupting a potential caspase cleavage site at aspartic residue (D)324 in RIPK1. Interestingly, replacing D324 with alanine (A) in RIPK1 results in midgestation lethality, similar to the embryonic defect in FADD-/- mice but in stark contrast to the normal embryogenesis of RIPK1-/- null mutant mice. Surprisingly, disrupting the downstream RIPK3 alone is insufficient to rescue RIPK1D324A/D324A mice from embryonic lethality, unless FADD is deleted simultaneously. Further analyses reveal a paradoxical role for RIPK1 in promoting caspase activation and apoptosis in embryos, a novel mechanism previously unappreciated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TRADD regulates perinatal development and adulthood survival in mice lacking RIPK1 and RIPK3.Nat Commun. 2019 Feb 11;10(1):705. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-08584-5. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30741936 Free PMC article.
-
RIPK1 prevents TRADD-driven, but TNFR1 independent, apoptosis during development.Cell Death Differ. 2019 May;26(5):877-889. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0166-8. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30185824 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage of RIPK1 by caspase-8 is crucial for limiting apoptosis and necroptosis.Nature. 2019 Oct;574(7778):428-431. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1548-x. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31511692
-
Developmental checkpoints guarded by regulated necrosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2125-36. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2188-z. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27056574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RIPK1 and RIPK3: critical regulators of inflammation and cell death.Trends Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;25(6):347-53. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Feb 4. Trends Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25662614 Review.
Cited by
-
Death by TNF: a road to inflammation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2023 May;23(5):289-303. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00792-3. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36380021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RIPK1 is a negative mediator in Aquaporin 1-driven triple-negative breast carcinoma progression and metastasis.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021 May 12;7(1):53. doi: 10.1038/s41523-021-00261-5. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33980862 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin E Can Ameliorate Oxidative Damage of Ovine Hepatocytes In Vitro by Regulating Genes Expression Associated with Apoptosis and Pyroptosis, but Not Ferroptosis.Molecules. 2021 Jul 27;26(15):4520. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154520. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361674 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase cleavage of RIPK3 after Asp333 is dispensable for mouse embryogenesis.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Feb;31(2):254-262. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01255-5. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 38191748 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 in SH-SY5Y cells with beta amyloid-induced neurotoxicity.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1434-1444. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17095. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35106914 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

