Exploitation of enrofloxacin-loaded docosanoic acid solid lipid nanoparticle suspension as oral and intramuscular sustained release formulations for pig
- PMID: 30880494
- PMCID: PMC6427631
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1580798
Exploitation of enrofloxacin-loaded docosanoic acid solid lipid nanoparticle suspension as oral and intramuscular sustained release formulations for pig
Abstract
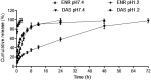
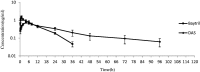
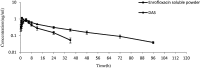
In our previous study, enrofloxacin-loaded docosanoic acid solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) could be effectively delivered to cells in vitro. In this study, its properties and exploitation as possible oral and intramuscular sustained release formulations for pigs were studied after being made into suspension. The re-dispersed time and sedimentation rate of the nanosuspension were 55 s and 1, respectively. It showed good stability when stored away from light and sustained release in pH = 7.4 PBS buffer. The suspension exhibited no irritation at the injection site and good palatability. Compared with commercial injection and soluble powder, the nanosuspension increased the bioavailability of enrofloxacin by 1.63 and 2.38 folds, and extended the mean residence time (MRT) of the drug from 11.27 and 12.33 to 37.76 and 35.15 h after intragastric and intramuscular administration, respectively. These results suggest that docosanoic acid SLN suspension (DAS) might be a promising oral and intramuscular sustained release formulation to enhance the pharmacological activity of enrofloxacin.
Keywords: Enrofloxacin; docosanoic acid-solid lipid nanoparticles; intramuscular formulation; oral formulation; suspension.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Solid lipid nanoparticles with enteric coating for improving stability, palatability, and oral bioavailability of enrofloxacin.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Mar 1;14:1619-1631. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S183479. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30880969 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: influences of fatty acids.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011 Apr 1;83(2):382-7. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.12.014. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011. PMID: 21215599
-
A novel monolithic controlled delivery system of resveratrol for enhanced hepatoprotection: nanoformulation development, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016 Sep;42(9):1524-36. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2016.1151032. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2016. PMID: 26902951
-
Novel oral suspensions: a review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2014;11(3):338-58. doi: 10.2174/1567201811666140113114926. Curr Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24410269 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Long-Acting Aqueous Nano-/Microsuspensions After Intramuscular Administration in Different Animal Species and Humans-a Review.AAPS J. 2022 Dec 1;25(1):4. doi: 10.1208/s12248-022-00771-5. AAPS J. 2022. PMID: 36456852 Review.
Cited by
-
Cefquinome Sulfate Oily Nanosuspension Designed for Improving its Bioavailability in the Treatment of Veterinary Infections.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Jun 2;17:2535-2553. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S348822. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35677677 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle Drug Delivery Systems for α-Mangostin.Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2020 Apr 1;13:23-36. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S243017. eCollection 2020. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2020. PMID: 32280205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiolabeled Trastuzumab Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Breast Cancer Cell: in Vitro and in Vivo Studies.ACS Omega. 2022 Aug 19;7(34):30015-30027. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03023. eCollection 2022 Aug 30. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36061662 Free PMC article.
-
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Duodenum _targeted Oral Delivery of Tilmicosin.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Aug 4;12(8):731. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12080731. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32759764 Free PMC article.
-
pH-driven entrapment of enrofloxacin in casein-based nanoparticles for the enhancement of oral bioavailability.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Apr 7;9(8):4057-4067. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2224. eCollection 2021 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34401057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari MJ, Anwer MK, Jamil S, et al. (2016). Enhanced oral bioavailability of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: pharmacokinetic bioavailability of insulin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles in diabetic rats. Drug Deliv 23:1972–9. - PubMed
-
- Elmas M, Uney K, Yazar E, et al. (2007). Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin following intravenousand intramuscular administration in Angora rabbits. Res Vet Sci 82:242–5. - PubMed
-
- Elsheikh HA, Taha AAW, Khalafallah AI, Osman IAM (2002). Disposition kinetics of enrofloxacin (Baytril 5%) in sheep and goatsfollowing intravenous and intramuscular injection using a microbiologicalassay. Res Vet Sci 73:125–9. - PubMed
-
- Haritova A, Lashev L, Pashov D (2003). Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin in lactating sheep. Res Vet Sci 74:241–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
