How does empagliflozin improve arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? Sub analysis of a clinical trial
- PMID: 30922297
- PMCID: PMC6440009
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-019-0839-8
How does empagliflozin improve arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? Sub analysis of a clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Empagliflozin has been shown to reduce cardiovascular mortality, but the underlying pathogenetic mechanisms are poorly understood. It was previously demonstrated that empagliflozin improved arterial stiffness.
Methods: Our analysis comprising 58 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus identifies factors triggering the improvement of arterial stiffness. All patients participated in an investigator-initiated, prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, interventional clinical trial ( http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov : NCT02471963, registered 15th June 2015, retrospectively registered) and received either 6-weeks treatment with 25 mg empagliflozin orally once daily or placebo (crossover). Central systolic pressure and central pulse pressure were recorded by the SphygmoCor System (AtCor Medical). Now, we investigated the impact of parameters of glucose metabolism, volume status, sympathetic activation, lipids, uric acid, blood pressure and inflammation on vascular parameters of arterial stiffness using multivariate regression analysis.
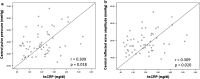
Results: As previously reported, therapy with empagliflozin improved arterial stiffness as indicated by reduced central systolic blood pressure (113.6 ± 12.1 vs 118.6 ± 12.9 mmHg, p < 0.001), central pulse pressure (39.1 ± 10.2 vs 41.9 ± 10.7 mmHg, p = 0.027) forward (27.1 ± 5.69 vs 28.7 ± 6.23 mmHg, p = 0.031) as well as reflected wave amplitude (18.9 ± 5.98 vs 20.3 ± 5.97 mmHg, p = 0.045) compared to placebo. The multivariate regression analysis included age, sex and change between empagliflozin and placebo therapy of the following parameters: HbA1c, copeptin, hematocrit, heart rate, LDL-cholesterol, uric acid, systolic 24-h ambulatory blood pressure and high sensitive CRP (hsCRP). Besides the influence of age (beta = - 0.259, p = 0.054), sex (beta = 0.292, p = 0.040) and change in systolic 24-h ambulatory blood pressure (beta = 0.364, p = 0.019), the change of hsCRP (beta = 0.305, p = 0.033) emerged as a significant determinant of the empagliflozin induced reduction in arterial stiffness (placebo corrected). When replacing HbA1c with fasting plasma glucose in the multivariate regression analysis, a similar effect of the change in hsCRP (beta = 0.347, p = 0.017) on arterial stiffness parameters was found.
Conclusion: Besides age and sex, change in systolic 24-h ambulatory blood pressure and change in hsCRP were determinants of the empagliflozin induced improvement of vascular parameters of arterial stiffness, whereas parameters of change in glucose metabolism and volume status had no significant influence. Our analysis suggests that empagliflozin exerts, at least to some extent, its beneficial vascular effects via anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Trial registration http://www.ClinicalTrials.gov : NCT02471963, registered 15th June 2015, retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Central hemodynamics; Diabetes mellitus type 2; Empagliflozin; Inflammation; Vascular function.
Conflict of interest statement
RES has received speaker fees and advisory board fees from Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co.KG during the conduct of the study. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of empagliflozin on ketone bodies in patients with stable chronic heart failure.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Nov 9;20(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01410-7. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34753480 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin improves blood pressure and vascular function in type 2 diabetes.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020 Nov 1;6(6):364-371. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvz078. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31816038 Clinical Trial.
-
Empagliflozin on top of metformin treatment improves arterial function in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018 Dec 3;17(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0797-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 30509271 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diabetes Mellitus, Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Disease: Clinical Implications and the Influence of SGLT2i.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2021;19(2):233-240. doi: 10.2174/1570161118666200317150359. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32183678 Review.
-
Empagliflozin in the treatment of heart failure.Future Cardiol. 2024 Apr 25;20(5-6):251-261. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2024.2360818. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Future Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38865086 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Additional Treatment with Empagliflozin or Semaglutide on Endothelial Function and Arterial Stiffness in Subjects with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-ENDIS Study.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 14;15(7):1945. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071945. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514131 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction with SGLT2 inhibitors: new therapy standard?Herz. 2022 Oct;47(5):395-400. doi: 10.1007/s00059-022-05134-6. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Herz. 2022. PMID: 36018379 Review. English.
-
An Overview of the Cardiorenal Protective Mechanisms of SGLT2 Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3651. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073651. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Vascular Cell Function and Arterial Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8786. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168786. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular and metabolic effects of SGLT2i and GLP-1 in heart failure patients.Heart Fail Rev. 2023 May;28(3):733-744. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10157-y. Epub 2021 Aug 11. Heart Fail Rev. 2023. PMID: 34379224 Review.
References
-
- Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, Jensen GV, Parving HH, Pedersen O. Multifactorial intervention and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(5):383–393. - PubMed
-
- Ott C, Schmid A, Toennes SW, Ditting T, Veelken R, Uder M, Schmieder RE. Central pulse pressure predicts BP reduction after renal denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension. EuroIntervention. 2015;11(1):110–116. - PubMed
-
- Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, Pannier B, Vlachopoulos C, Wilkinson I, Struijker-Boudier H, et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J. 2006;27(21):2588–2605. - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Bohm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) J Hypertens. 2013;31(7):1281–1357. - PubMed
-
- Weber T, Wassertheurer S, Rammer M, Haiden A, Hametner B, Eber B. Wave reflections, assessed with a novel method for pulse wave separation, are associated with end-organ damage and clinical outcomes. Hypertension. 2012;60(2):534–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

