Distribution of antibiotic resistance and virulence factors among the bacteria isolated from diseased Etroplus suratensis
- PMID: 30944785
- PMCID: PMC6419682
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-019-1654-3
Distribution of antibiotic resistance and virulence factors among the bacteria isolated from diseased Etroplus suratensis
Abstract
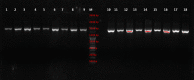
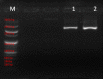
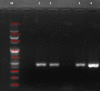
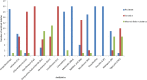
Considering the emerging concern with the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) evolution, the study has been designed to identify the antibiotic resistance and virulence properties of culturable bacteria isolated from the diseased fish Etroplus suratensis. This has resulted in the purification of 18 morphologically distinct bacterial isolates which were identified by both biochemical and molecular methods. Antibiotic resistance analysis showed the resistance of these isolates to multiple antibiotics and remarkable evolution of AMR. Further screening for virulence factors confirmed five isolates to be positive for haemolytic activity, eight with caseinase, four with DNase, one with gelatinase and three with biofilm-forming properties. In addition to these, the isolates were subjected to PCR-based screening to detect the presence of genes coding for aerolysin and haemolysin. Results showed the presence aerolysin gene in the isolates ESS3.2, ESS3.8, ESI3.3 and ESS3.6, while haemolysin gene was observed to be present in ESG3.1 and ESI3.2. The observed results hence indicate the need for frequent monitoring of these properties among bacterial isolates from diverse environment especially those associated with edible fish.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Aquaculture; Etroplus suratensis; Virulence mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of virulence properties and multi-drug resistance profiles in motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from zebrafish (Danio rerio).Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018 Dec;67(6):598-605. doi: 10.1111/lam.13075. Epub 2018 Nov 12. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30229985
-
Identity and virulence properties of Aeromonas isolates from diseased fish, healthy controls and water environment in China.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012 Sep;55(3):224-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2012.03281.x. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22725694
-
Diversity of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens from a freshwater ornamental fish farm.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jul;71(1):108-116. doi: 10.1111/lam.13231. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31602688
-
Comparative Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance, Integrons, and Virulence Genes Among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Positive Laribacter hongkongensis from Edible Frogs and Freshwater Fish.Microb Drug Resist. 2019 Jul/Aug;25(6):855-864. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0366. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Microb Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 30767721
-
Unravelling the menace: detection of antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2020 Jul;71(1):26-38. doi: 10.1111/lam.13292. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32248555 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacteriophages in the Control of Aeromonas sp. in Aquaculture Systems: An Integrative View.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 27;11(2):163. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020163. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of Aeromonas Isolates from Ornamental Fish: Species, Virulence Genes, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 16;12(1):176. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010176. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38258002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC, Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1996;45(4):493–496. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

