Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats
- PMID: 31010055
- PMCID: PMC6514672
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20081951
Dose-Dependent Effect of Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment on Burn-Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats
Abstract
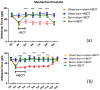
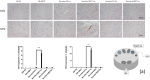
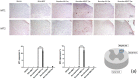
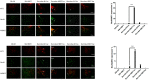
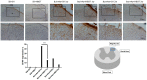
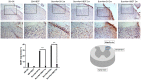
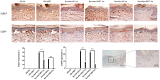
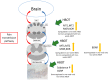
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) has been used to reduce neuropathic pain. Melatonin and opioid receptors are involved in neuropathic pain, but it is not known if HBOT works through these pathways to achieve its antinociceptive effect. We divided anesthetized rats into two treatment and three sham groups. The two treatment groups received third-degree burns on their right hind paws, one treated in a hyperbaric chamber for a week and the other for two weeks. We evaluated the mechanical paw-withdrawal threshold (MWT) and expression of melatonin receptor 1 (MT1), melatonin receptor 2 (MT2), μ (MOR) and κ (KOR) opioid receptor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), Substance P, and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in cuneate nucleus, dorsal horn, and hind paw skin by immunohistochemical, immunofluorescence assays and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The group receiving one-week HBOT had increased expressions of MT1, MT2, MOR and KOR and decreased expressions of BDNF, Substance P, and CGRP. Their mechanically measured pain levels returned to normal within a week and lasted three weeks. This anti-allodynia effect lasted twice as long in those treated for two weeks. Our findings suggest that increasing the duration of HBOT can reduce burn-induced mechanical allodynia for an extended period of time in rats. The upregulation of melatonin and opioid receptors observed after one week of HBOT suggests they may be partly involved in attenuation of the mechanical allodynia. Downregulation of BDNF, substance P and CGRP may have also contributed to the overall beneficial effect of HBOT.
Keywords: cuneate nucleus; hyperbaric oxygen; melatonin; neuropathic pain; opioid receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Early Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment Attenuates Burn-Induced Neuroinflammation by Inhibiting the Galectin-3-Dependent Toll-Like Receptor-4 Pathway in a Rat Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 27;19(8):2195. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082195. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30060489 Free PMC article.
-
[Melatonin receptor 2 mediated spinal dorsal horn astrocytes IL-17 inhibition contributes to electroacupuncture analgesia in neuropathic pain rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Jul 25;46(7):562-9. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.201158. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34369675 Chinese.
-
Contribution of the spinal cord BDNF to the development of neuropathic pain by activation of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in rats with spinal nerve ligation.Exp Neurol. 2010 Apr;222(2):256-66. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.01.003. Epub 2010 Jan 14. Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20079352
-
Mechanistic Rationale and Clinical Efficacy of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Chronic Neuropathic Pain: An Evidence-Based Narrative Review.Pain Res Manag. 2021 Apr 22;2021:8817504. doi: 10.1155/2021/8817504. eCollection 2021. Pain Res Manag. 2021. PMID: 33976752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the treatment of neuropathic pain with hyperbaric oxygen.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2021 First Quarter;48(1):13-23. doi: 10.22462/01.03.2021.2. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2021. PMID: 33648029 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous Administration of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Antioxidant Supplementation with Filipendula ulmaria Extract in the Treatment of Thermal Skin Injuries Alters Nociceptive Signalling and Wound Healing.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Sep 17;59(9):1676. doi: 10.3390/medicina59091676. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37763795 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of burn injury on the central nervous system.Burns Trauma. 2024 Feb 1;12:tkad037. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkad037. eCollection 2024. Burns Trauma. 2024. PMID: 38312739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Attenuates Burn-Induced Denervated Muscle Atrophy.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Oct 25;18(16):3821-3830. doi: 10.7150/ijms.65976. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34790058 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Melatonin in the Regulation of Pain.J Pain Res. 2020 Feb 7;13:331-343. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S228577. eCollection 2020. J Pain Res. 2020. PMID: 32104055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex Hippocampal Response to Thermal Skin Injury and Protocols with Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy and Filipendula ulmaria Extract in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 6;25(5):3033. doi: 10.3390/ijms25053033. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuo S.C., Hsu C.K., Tsai C.T., Chieh M.J. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Hu Li Za Zhi. 2018;65:11–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

