Usefulness of percutaneous microwave ablation for large non-small cell lung cancer: A preliminary report
- PMID: 31289539
- PMCID: PMC6546981
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10375
Usefulness of percutaneous microwave ablation for large non-small cell lung cancer: A preliminary report
Abstract
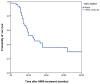
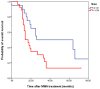
The role of microwave ablation (MWA) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains ill-defined. This retrospective study evaluated the oncological outcomes of CT-guided MWA in patients with large NSCLC. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to evaluate overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS). The log-rank test was used to compare survival between patients with an NSCLC size greater or smaller than 4 cm. The likelihood of local tumor progression (LTP) was analyzed using a multivariable regression model. A total of 53 patients with 65 tumors were analyzed. The mean tumor size was 5.0±1.8 cm. At the 1-month CT scan, complete tumor ablation was observed in 44.6% of cases. In 18.5% of cases a redo-MWA session was carried out, while in 4.6%, a third MWA was necessary to obtain complete tumor necrosis. The mean follow-up was 28.1±20.6 months with a median duration of 21.5 months. The 1-year, 2-year, 3-year and 5-year OS rates were 78.2, 48.3, 34.8 and 18.3%, respectively. The median CSS was 25 months (95% CI 15.5-34.5). The 1-year, 2-year, 3-year and 5-year CSS rates were 84.3, 53.7, 42.1 and 30.0%, respectively. OS in patients with tumor size ≥4 cm was significantly lower when compared with those having smaller tumors (P=0.03). LTP was observed in 19 patients (35.8%). Incomplete tumor ablation [odds ratio (OR) 6.57; P<0.05] and tumor size ≥4 cm (OR 0.18; P<0.05) were significant independent predictors of LTP. In conclusion, CT-guided MWA may represent a useful tool in the multimodality treatment of patients with large advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: CT-guided ablation; microwave ablation; multimodality cancer treatment; non-small cell lung cancer; non-surgical treatment; percutaneous treatment.
Figures
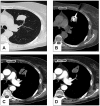
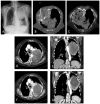
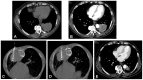
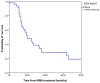
Similar articles
-
Safety and clinical outcomes of computed tomography-guided percutaneous microwave ablation in patients aged 80 years and older with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter retrospective study.Thorac Cancer. 2019 Dec;10(12):2236-2242. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13209. Epub 2019 Nov 3. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31679181 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between computed tomography-guided percutaneous microwave ablation and thoracoscopic lobectomy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Nov;9(11):1376-1382. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12842. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30152596 Free PMC article.
-
Microwave Ablation in the Management of Colorectal Cancer Pulmonary Metastases.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018 Oct;41(10):1530-1544. doi: 10.1007/s00270-018-2000-6. Epub 2018 May 29. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29845348 Free PMC article.
-
The local efficacy and influencing factors of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation in colorectal liver metastases: a review of a 4-year experience at a single center.Int J Hyperthermia. 2019;36(1):36-43. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1528511. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Int J Hyperthermia. 2019. PMID: 30489175 Review.
-
Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in Liver Tumors: An Update.Oncologist. 2019 Oct;24(10):e990-e1005. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0337. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Oncologist. 2019. PMID: 31217342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microwave ablation for non-small cell lung cancer with synchronous solitary extracranial metastasis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 May;146(5):1361-1367. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03176-z. Epub 2020 Mar 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32146563
-
Synchronous Microwave Ablation Combined With Cisplatin Intratumoral Chemotherapy for Large Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 28;12:955545. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.955545. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35965525 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and local efficacy of computed tomography-guided microwave ablation for treating early-stage non-small cell lung cancer adjacent to bronchovascular bundles.Eur Radiol. 2024 Jan;34(1):236-246. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09997-z. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37505251
-
CT-based radiomics models may predict the early efficacy of microwave ablation in malignant lung tumors.Cancer Imaging. 2023 Jun 12;23(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s40644-023-00571-w. Cancer Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37308918 Free PMC article.
-
Transbronchial microwave ablation of lung nodules with electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy guidance-a novel technique and initial experience with 30 cases.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Apr;10(4):1608-1622. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-1231. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34012778 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
