Therapeutic _targeting of 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: inhibition and beyond
- PMID: 31388135
- PMCID: PMC6773486
- DOI: 10.1038/s41573-019-0033-4
Therapeutic _targeting of 3',5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: inhibition and beyond
Abstract
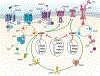
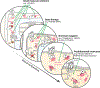
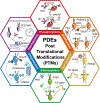
Phosphodiesterases (PDEs), enzymes that degrade 3',5'-cyclic nucleotides, are being pursued as therapeutic _targets for several diseases, including those affecting the nervous system, the cardiovascular system, fertility, immunity, cancer and metabolism. Clinical development programmes have focused exclusively on catalytic inhibition, which continues to be a strong focus of ongoing drug discovery efforts. However, emerging evidence supports novel strategies to therapeutically _target PDE function, including enhancing catalytic activity, normalizing altered compartmentalization and modulating post-translational modifications, as well as the potential use of PDEs as disease biomarkers. Importantly, a more refined appreciation of the intramolecular mechanisms regulating PDE function and trafficking is emerging, making these pioneering drug discovery efforts tractable.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: important signaling modulators and therapeutic _targets.Oral Dis. 2015 Jan;21(1):e25-50. doi: 10.1111/odi.12275. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Oral Dis. 2015. PMID: 25056711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDE inhibitors: a new approach to treat metabolic syndrome?Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011 Dec;11(6):698-706. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2011.09.012. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22018840 Review.
-
Nanodomain Regulation of Cardiac Cyclic Nucleotide Signaling by Phosphodiesterases.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Jan 6;57:455-479. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010716-104756. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27732797 Review.
-
[Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: therapeutic _targets in cardiac hypertrophy and failure].Med Sci (Paris). 2024 Jun-Jul;40(6-7):534-543. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2024083. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Med Sci (Paris). 2024. PMID: 38986098 Review. French.
-
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S252-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706495. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16402111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphodiesterase inhibition and Gucy2C activation enhance tyrosine hydroxylase Ser40 phosphorylation and improve 6-hydroxydopamine-induced motor deficits.Cell Biosci. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01312-7. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39456033 Free PMC article.
-
Going Rogue: Mechanisms, Regulation, and Roles of Mutationally Activated Gα in Human Cancer.Mol Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 17;106(5):198-215. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.124.000743. Mol Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39187387 Review.
-
Pentoxifylline as an adjunctive in treatment of negative symptoms in chronic schizophrenia: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023 Jan;29(1):354-364. doi: 10.1111/cns.14010. Epub 2022 Nov 7. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023. Retraction in: CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Mar;30(3):e14668. doi: 10.1111/cns.14668 PMID: 36341700 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
cGMP: a unique 2nd messenger molecule - recent developments in cGMP research and development.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;393(2):287-302. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01779-z. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31853617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using the Proteomics Toolbox to Resolve Topology and Dynamics of Compartmentalized cAMP Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 28;24(5):4667. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054667. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schneider EH & Seifert R Inactivation of Non-canonical Cyclic Nucleotides: Hydrolysis and Transport. Handb Exp Pharmacol 238, 169–205 (2017). - PubMed
-
Helpful review on the role PDEs play in regulating non-canonical cyclic nucleotides.
-
- Seifert R cCMP and cUMP Across the Tree of Life: From cCMP and cUMP Generators to cCMP- and cUMP-Regulated Cell Functions. Handb Exp Pharmacol 238, 3–23 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Patel NS et al. Identification of new PDE9A isoforms and how their expression and subcellular compartmentalization in the brain change across the life span. Neurobiol Aging 65, 217–234 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
First report showing that the subcellular compartmentalization of a PDE family differs depending on the specific isoform, age, and tissue investigated.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

