Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms
- PMID: 31441146
- PMCID: PMC6798127
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3715
Toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms
Abstract
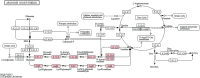
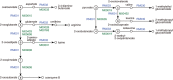
In this era of high-throughput biology, bioinformatics has become a major discipline for making sense out of large-scale datasets. Bioinformatics is usually considered as a practical field developing databases and software tools for supporting other fields, rather than a fundamental scientific discipline for uncovering principles of biology. The KEGG resource that we have been developing is a reference knowledge base for biological interpretation of genome sequences and other high-throughput data. It is now one of the most utilized biological databases because of its practical values. For me personally, KEGG is a step toward understanding the origin and evolution of cellular organisms.
Keywords: KEGG; KEGG MEDICUS; KEGG module; pathway mapping; reaction module.
© 2019 The Protein Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KEGG Bioinformatics Resource for Plant Genomics and Metabolomics.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1374:55-70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3167-5_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26519400
-
Molecular network analysis of diseases and drugs in KEGG.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;939:263-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-107-3_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23192552
-
KEGG Mapper for inferring cellular functions from protein sequences.Protein Sci. 2020 Jan;29(1):28-35. doi: 10.1002/pro.3711. Epub 2019 Aug 29. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 31423653 Free PMC article.
-
KEGG as a glycome informatics resource.Glycobiology. 2006 May;16(5):63R-70R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwj010. Epub 2005 Jul 13. Glycobiology. 2006. PMID: 16014746 Review.
-
Knowledge-Based Analysis of Protein Interaction Networks in Neurodegenerative Diseases.In: Alzate O, editor. Neuroproteomics. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 9. In: Alzate O, editor. Neuroproteomics. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2010. Chapter 9. PMID: 21882442 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel gene signatures for stage classification of the squamous cell carcinoma of the lung.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 1;11(1):4835. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83668-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649335 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating immune dysregulation and hub genes in septic cardiomyopathy development.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 16;14(1):21608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72724-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39294340 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic immune evasion patterns predict temozolomide sensitivity and immunotherapy response in lower-grade gliomas.BMC Cancer. 2022 Sep 12;22(1):973. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09984-5. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36096781 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Connexin36 Phosphorylation in AII Amacrine Cell Coupling of the Mouse Myopic Retina.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jun 1;14:124. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00124. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32547367 Free PMC article.
-
SPAG7 deletion causes intrauterine growth restriction, resulting in adulthood obesity and metabolic dysfunction.Elife. 2024 Jul 26;12:RP91114. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91114. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39056292 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanehisa M (2000) Post‐genome Informatics, Oxford University Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

