Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia
- PMID: 31491916
- PMCID: PMC6780172
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8091389
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Prescription According to Reimbursement Constraints and Guideline Recommendations in Catalonia
Abstract
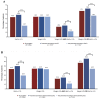
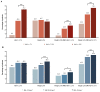
To assess the clinical characteristics, the prescription pattern of GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) users, and HbA1c and weight change, we retrospectively assessed patients with type 2 diabetes by initiating GLP-1RA as an add-on to the standard of care in Catalonia. The mean change from the baseline in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and weight at 6 and 12 months of therapy was calculated, and we assessed the predictors of the HbA1c reduction of ≥1% and/or the weight reduction of ≥3% as recommended by the Catalan Health Service. In 2854 patients who initiated a GLP-1RA during 2014 and 2015, the overall mean HbA1c values were reduced from the baseline by -0.84% (SD = 1.66) (-9.2 mmol/mol) and lost on average 2.73 kg (SD = 6.2). About 44% percent of patients decreased their HbA1c by ≥1%; 44% decreased their weight by ≥3%; and only 22% met both of them together. The odds of achieving a reduction of ≥1% in initial HbA1c were two-fold higher for patients with higher baseline levels, and the likelihood of a reduction of ≥3% in the initial weight was associated with a higher BMI at the baseline, but they were independent of each other. The composite outcome (_target 1% HbA1c reduction and 3% weight loss) to evaluate both the GLP-1RA clinical benefit and treatment withdrawal should be judged from a patient-centered approach.
Keywords: GLP-1 analogue; glycaemic control; observational study; primary care; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results. M. M.-C. has received an advisory honorarium from Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; he has received a speaker honorarium from Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Lilly, Menarini, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; he has received research grants to the institution from Astra-Zeneca, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi. J. F.-N. has received advisory and or speaking fees from Astra-Zeneca, Ascensia, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; he has received research grants to the institution from Astra-Zeneca, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Boehringer. D.M. has received advisory and/or speaking fees from Astra-Zeneca, Ascensia, Boehringer Ingelheim, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi; he has received research grants to the institution from Astra-Zeneca, GSK, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Boehringer. E.O. has received advisory and or speaking fees from Astra-Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, MSD, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, and Amgen; he has received research grants to the institution from MSD and Amgen. J.R., B.V., JA.V. and M.G. have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucagon-like-1 receptor agonists and sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors combination-are we exploiting their full potential in a real life setting?World J Diabetes. 2020 Nov 15;11(11):540-552. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i11.540. World J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 33269065 Free PMC article.
-
Glycaemic efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors as add-on therapy to metformin in subjects with type 2 diabetes-a review and meta analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012 Aug;14(8):762-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2012.01603.x. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012. PMID: 22471248 Review.
-
A Retrospective Study of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for the Management of Diabetes After Transplantation.Diabetes Ther. 2020 Apr;11(4):987-994. doi: 10.1007/s13300-020-00786-1. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Diabetes Ther. 2020. PMID: 32072430 Free PMC article.
-
C-Peptide Area Under the Curve at Glucagon Stimulation Test Predicts Glucose Improvements by GLP-1 Receptor Analogue: A Retrospective Observational Study.Diabetes Ther. 2019 Apr;10(2):673-681. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-0586-6. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Diabetes Ther. 2019. PMID: 30788807 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in type 1 diabetes mellitus.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019 Oct 15;76(21):1739-1748. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxz179. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31612934 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Approaches in Chronic Renal Failure without Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 18;11(10):2828. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102828. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Acting Injectable GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Perspectives from Clinical Practice.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Nov 9;13:4221-4234. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S216054. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33204129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term trends in the prescription of antidiabetic drugs: real-world evidence from the Diabetes Registry Tyrol 2012-2018.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 Sep;8(1):e001279. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001279. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 32873600 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of patient-specific factors contributing to effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists.J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020 Nov-Dec;60(6):937-942. doi: 10.1016/j.japh.2020.06.023. Epub 2020 Aug 8. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003). 2020. PMID: 32778515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garber A.J., Abrahamson M.J., Barzilay J.I., Blonde L., Bloomgarden Z.T., Bush M.A., Dagogo-Jack S., DeFronzo R.A., Einhorn D., Fonseca V.A., et al. Consensus Statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the Comprehensive Type 2 Diabetes Management Algorithm--2016 Executive Summary. Endocr. Pract. 2016;22:84–113. doi: 10.4158/EP151126.CS. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davies M.J., D’Alessio D.A., Fradkin J., Kernan W.N., Mathieu C., Mingrone G., Rossing P., Tsapas A., Wexler D.J., Buse J.B. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2018. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetes Care. 2018 doi: 10.2337/dci18-0033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

