Smad7 Binds Differently to Individual and Tandem WW3 and WW4 Domains of WWP2 Ubiquitin Ligase Isoforms
- PMID: 31546607
- PMCID: PMC6801763
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20194682
Smad7 Binds Differently to Individual and Tandem WW3 and WW4 Domains of WWP2 Ubiquitin Ligase Isoforms
Abstract
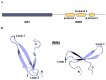
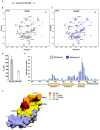
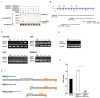
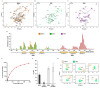
WWP2 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that differentially regulates the contextual tumour suppressor/progressor TGFβ signalling pathway by alternate isoform expression. WWP2 isoforms select signal transducer Smad2/3 or inhibitor Smad7 substrates for degradation through different compositions of protein-protein interaction WW domains. The WW4 domain-containing WWP2-C induces Smad7 turnover in vivo and positively regulates the metastatic epithelial-mesenchymal transition programme. This activity and the overexpression of these isoforms in human cancers make them candidates for therapeutic intervention. Here, we use NMR spectroscopy to solve the solution structure of the WWP2 WW4 domain and observe the binding characteristics of Smad7 substrate peptide. We also reveal that WW4 has an enhanced affinity for a Smad7 peptide phosphorylated at serine 206 adjacent to the PPxY motif. Using the same approach, we show that the WW3 domain also binds Smad7 and has significantly enhanced Smad7 binding affinity when expressed in tandem with the WW4 domain. Furthermore, and relevant to these biophysical findings, we present evidence for a novel WWP2 isoform (WWP2C-ΔHECT) comprising WW3-WW4 tandem domains and a truncated HECT domain that can inhibit TGFβ signalling pathway activity, providing a further layer of complexity and feedback to the WWP2 regulatory apparatus. Collectively, our data reveal a structural platform for Smad substrate selection by WWP2 isoform WW domains that may be significant in the context of WWP2 isoform switching linked to tumorigenesis.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; NEDD4; TGFβ signalling; WW domain; protein interaction; smad; smad7; transforming growth factor beta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Selective _targeting of activating and inhibitory Smads by distinct WWP2 ubiquitin ligase isoforms differentially modulates TGFβ signalling and EMT.Oncogene. 2011 May 26;30(21):2451-62. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.617. Epub 2011 Jan 24. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21258410 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling of tandem Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor (Smurf) WW domains modulates _target specificity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 26;107(43):18404-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003023107. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20937913 Free PMC article.
-
Novel WWP2 ubiquitin ligase isoforms as potential prognostic markers and molecular _targets in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1832(12):2127-35. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23938591
-
The role of WWP1 and WWP2 in bone/cartilage development and diseases.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Nov;479(11):2907-2919. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04917-7. Epub 2024 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38252355 Review.
-
WWP1: a versatile ubiquitin E3 ligase in signaling and diseases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 May;69(9):1425-34. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0871-7. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22051607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Interactions between Two LMP2A PY Motifs of EBV and WW Domains of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase AIP4.Life (Basel). 2021 Apr 22;11(5):379. doi: 10.3390/life11050379. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922228 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting PY motif-mediated protein-protein interactions in the Nedd4 family of ubiquitin ligases.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 12;16(10):e0258315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258315. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34637467 Free PMC article.
-
Specific isoforms of the ubiquitin ligase gene WWP2 are _targets of osteoarthritis genetic risk via a differentially methylated DNA sequence.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Apr 3;26(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03315-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38570801 Free PMC article.
-
SMADS-Mediate Molecular Mechanisms in Sjögren's Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 21;22(6):3203. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063203. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33801157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Transcription Inhibitor 1E7-03 Decreases Nucleophosmin Phosphorylation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023 Feb;22(2):100488. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2022.100488. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 36563749 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

