Functional RNAi Screens Define Distinct Protein Kinase Vulnerabilities in EGFR-Dependent HNSCC Cell Lines
- PMID: 31554698
- PMCID: PMC7385532
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.119.117804
Functional RNAi Screens Define Distinct Protein Kinase Vulnerabilities in EGFR-Dependent HNSCC Cell Lines
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Functional RNAi Screens Define Distinct Protein Kinase Vulnerabilities in EGFR-Dependent HNSCC Cell Lines".Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;98(3):184. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.117804err. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32759351 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
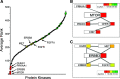
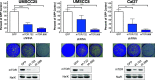
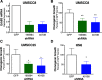
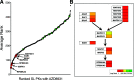
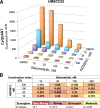
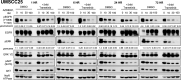
The inhibitory epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody, cetuximab, is an approved therapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Despite tumor response observed in some HNSCC patients, cetuximab alone or combined with radio- or chemotherapy fails to yield long-term control or cures. We hypothesize that a flexible receptor tyrosine kinase coactivation signaling network supports HNSCC survival in the setting of EGFR blockade, and that drugs disrupting this network will provide superior tumor control when combined with EGFR inhibitors. In this work, we submitted EGFR-dependent HNSCC cell lines to RNA interference-based functional genomics screens to identify, in an unbiased fashion, essential protein kinases for growth and survival as well as synthetic lethal _targets for combined inhibition with EGFR antagonists. Mechanistic _target of rapamycin kinase (MTOR) and erythroblastosis oncogene B (ERBB)3 were identified as high-ranking essential kinase hits in the HNSCC cell lines. MTOR dependency was confirmed by distinct short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) and high sensitivity of the cell lines to AZD8055, whereas ERBB3 dependency was validated by shRNA-mediated silencing. Furthermore, a synthetic lethal kinome shRNA screen with a pan-ERBB inhibitor, AZD8931, identified multiple components of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, consistent with ERK reactivation and/or incomplete ERK pathway inhibition in response to EGFR inhibitor monotherapy. As validation, distinct mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors yielded synergistic growth inhibition when combined with the EGFR inhibitors, gefitinib and AZD8931. The findings identify ERBB3 and MTOR as important pharmacological vulnerabilities in HNSCC and support combining MEK and EGFR inhibitors to enhance clinical efficacy in HNSCC. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Many cancers are driven by nonmutated receptor tyrosine kinase coactivation networks that defy full inhibition with single _targeted drugs. This study identifies erythroblastosis oncogene B (ERBB)3 as an essential protein kinase in epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent head and neck squamous cell cancer (HNSCC) cell lines and a synthetic lethal interaction with the extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway that provides a rationale for combining pan-ERBB and mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors as a therapeutic approach in subsets of HNSCC.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced interferon pathway signaling in the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma therapeutic response.J Transl Med. 2021 Jan 23;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02706-8. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33485341 Free PMC article.
-
Co-_targeting EGFR and IKKβ/NF-κB signalling pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a potential novel therapy for head and neck squamous cell cancer.Br J Cancer. 2019 Feb;120(3):306-316. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0351-z. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Br J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30585254 Free PMC article.
-
ANO1/TMEM16A interacts with EGFR and correlates with sensitivity to EGFR-_targeting therapy in head and neck cancer.Onco_target. 2015 Apr 20;6(11):9173-88. doi: 10.18632/onco_target.3277. Onco_target. 2015. PMID: 25823819 Free PMC article.
-
Current challenges and clinical investigations of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)- and ErbB family-_targeted agents in the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).Cancer Treat Rev. 2014 May;40(4):567-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Cancer Treat Rev. 2014. PMID: 24216225 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin: molecular bases for EGFR-_targeted therapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2011 Jun 15;207(6):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Pathol Res Pract. 2011. PMID: 21531084 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-induced interferon pathway signaling in the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma therapeutic response.J Transl Med. 2021 Jan 23;19(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02706-8. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33485341 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in Natural Compounds/siRNA Co-delivery Employing Nanovehicles for Cancer Therapy.ACS Comb Sci. 2020 Dec 14;22(12):669-700. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.0c00099. Epub 2020 Oct 23. ACS Comb Sci. 2020. PMID: 33095554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Input Dictates the Threshold of _targeting of the Integrin-Dependent Pathway in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jul 22;8:652. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00652. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32793596 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference screens discover proteases as synthetic lethal partners of PI3K inhibition in breast cancer cells.Theranostics. 2022 May 16;12(9):4348-4373. doi: 10.7150/thno.68299. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35673573 Free PMC article.
-
_targeted Treatment of Head and Neck (Pre)Cancer: Preclinical _target Identification and Development of Novel Therapeutic Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 3;13(11):2774. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112774. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, et al. (2006) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 354:567–578. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur RK, Raben D, Baselga J, Spencer SA, Zhu J, et al. (2010) Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol 11:21–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
