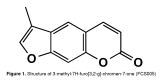
Coumarin analogue 3-methyl-7H-furo[3,2-g] chromen-7-one as a possible antiparkinsonian agent
- PMID: 31584763
- PMCID: PMC7357371
- DOI: 10.7705/biomedica.4299
Coumarin analogue 3-methyl-7H-furo[3,2-g] chromen-7-one as a possible antiparkinsonian agent
Abstract
Introduction: Parkinson's disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease. Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors are used in the treatment of this disease concomitantly with levodopa or as monotherapy. Several substituted coumarins have shown activity as inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B.
Objective: To evaluate the possible antiparkinsonian effects of the coumarin analogue FCS005 (3-methyl-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one) in mouse models, as well as its inhibitory activity towards monoamine oxidases (MAO) and its antioxidant activity.
Materials and methods: FCS005 was synthesized and the reversal of hypokinesia was evaluated in the reserpine and levodopa models. Moreover, in the haloperidol model, its anticataleptic effects were evaluated. Additionally, the monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity and antioxidant activity of FCS005 were evaluated using in vitro and ex vivo studies, respectively.
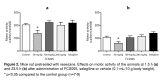
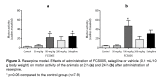
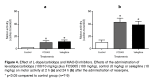
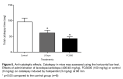
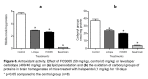
Results: FCS005 (100 mg/kg) caused the reversal of hypokinesia in the reserpine and levodopa models. This furocoumarin also presented anti-cataleptic effects at the same dose. Besides, it showed selective inhibitory activity towards the MAO-B isoform and antioxidant activity.
Conclusion: These results attribute interesting properties to the compound FCS005. It is important to continue research on this molecule considering that it could be a potential antiparkinsonian agent.
Introducción. El segundo trastorno neurodegenerativo más común es la enfermedad de Parkinson. Los inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa B se emplean en el tratamiento de esta enfermedad en monoterapia o concomitantemente con levodopa. Varios compuestos cumarínicos han mostrado actividad como inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa B. Objetivo. Evaluar los posibles efectos antiparkinsonianos del análogo de la cumarina FCS005 (3-methyl-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one) en modelos de ratones, la actividad inhibitoria frente a las monoamino oxidasas (MAO) y la actividad antioxidante. Materiales y métodos. Se sintetizó la furanocumarina FCS005 y, en los modelos de reserpina y levodopa, se evaluó si producía reversión de la hipocinesia; en el modelo de haloperidol se evaluaron sus efectos anticatalépticos. Además, se evaluó in vitro la actividad inhibidora de MAO y, ex vivo, la actividad antioxidante del compuesto FCS005. Resultados. El compuesto FCS005 en dosis de 100 mg/kg produjo la remisión de la hipocinesia en los modelos de reserpina y de levodopa. Esta furanocumarina presentó efectos anticatalépticos con la misma dosis. Además, mostró tener actividad inhibitoria selectiva sobre la MAO B, así como efectos antioxidantes. Conclusión. Los resultados evidenciaron propiedades interesantes del compuesto FCS005. Es importante continuar investigando esta molécula porque puede ser un potencial agente antiparkinsoniano.
Introducción.: El segundo trastorno neurodegenerativo más común es la enfermedad de Parkinson. Los inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa B se emplean en el tratamiento de esta enfermedad en monoterapia o concomitantemente con levodopa. Varios compuestos cumarínicos han mostrado actividad como inhibidores de la monoamino oxidasa B.
Objetivo.: Evaluar los posibles efectos antiparkinsonianos del análogo de la cumarina FCS005 (3-methyl-7H-furo [3,2-g ] chromen-7-one) en modelos de ratones, la actividad inhibitoria frente a las monoamino oxidasas (MAO) y la actividad antioxidante.
Materiales y métodos.: Se sintetizó la furanocumarina FCS005 y, en los modelos de reserpina y levodopa, se evaluó si producía reversión de la hipocinesia; en el modelo de haloperidol se evaluaron sus efectos anticatalépticos. Además, se evaluó in vitro la actividad inhibidora de MAO y, ex vivo, la actividad antioxidante del compuesto FCS005.
Resultados.: El compuesto FCS005 en dosis de 100 mg/kg produjo la remisión de la hipocinesia en los modelos de reserpina y de levodopa. Esta furanocumarina presentó efectos anticatalépticos con la misma dosis. Además, mostró tener actividad inhibitoria selectiva sobre la MAO B, así como efectos antioxidantes.
Conclusión.: Los resultados evidenciaron propiedades interesantes del compuesto FCS005. Es importante continuar investigando esta molécula porque puede ser un potencial agente antiparkinsoniano.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; monoamine oxidase; coumarins; models; animal; reserpine; levodopa; haloperidol; antioxidants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gamma-decanolactone: Preliminary evaluation as potential antiparkinsonian drug.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 5;906:174276. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174276. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34174267
-
Quercetin potentiates L-Dopa reversal of drug-induced catalepsy in rats: possible COMT/MAO inhibition.Pharmacology. 2003 Jun;68(2):81-8. doi: 10.1159/000069533. Pharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12711835
-
Antiparkinsonian effects of remacemide hydrochloride, a glutamate antagonist, in rodent and primate models of Parkinson's disease.Ann Neurol. 1994 Jun;35(6):655-61. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350605. Ann Neurol. 1994. PMID: 8210221
-
Defining the Role of the Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitors for Parkinson's Disease.CNS Drugs. 2015 Jun;29(6):433-41. doi: 10.1007/s40263-015-0249-8. CNS Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26164425 Review.
-
Rasagiline (TVP-1012): a new selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor for Parkinson's disease.Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006 Dec;4(4):330-46. doi: 10.1016/j.amjopharm.2006.12.001. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 17296539 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources