Comparison of Shaping Ability of Different Single-File Systems Using Microcomputed Tomography
- PMID: 32005040
- PMCID: PMC7069747
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1701393
Comparison of Shaping Ability of Different Single-File Systems Using Microcomputed Tomography
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the shaping ability of four different single-file systems using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
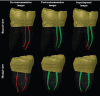
Materials and methods: Eighty mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals of permanent mandibular molars were randomly assigned to four groups according to the file used; WaveOne Gold, RECIPROC Blue, HyFlex EDM, and One Shape (n = 20). The samples were scanned using micro-CT for the preinstrumentation record; then the canals were instrumented and scanned for the postinstrumentation records.
Statistical analysis: The data were then analyzed statistically using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the level of significance set at α = 0.05.
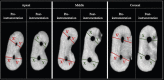
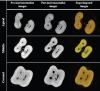
Results: The results of canal centering ratio and canal transportation showed that no significant difference was found among the four file groups at the middle and the coronal levels. However, a significant difference was found at the apical level (p < 0.05), where WaveOne Gold showed the best centering ratio and the least amount of canal transportation. The change in the canal volume was significant at the coronal level (p < 0.05), whereas the change in the canal volume was higher for the HyFlex EDM group than the other groups. No significant difference was found between the other groups at the apical level, middle level, or in the total percentage of canal volume.
Conclusion: WaveOne Gold produced a more centralized canal preparation with a lesser amount of transportation at the apical level. HyFlex EDM showed the highest canal volumetric change at the coronal level. The interim design of the endodontic files has a high impact on the behavior of the file inside the root canal.
Conflict of interest statement
This work should be attributed to Dental College of Georgia, Augusta University, Georgia, United States.All authors have contributed significantly and are in agreement with the manuscript.None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Canal-centering Ability and Apical Transportation of Hyflex-EDM, OneShape, WaveOne Gold, and Reciproc Files: An Ex Vivo Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2023 Oct 1;24(10):802-808. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3571. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2023. PMID: 38152914
-
Evaluation of apical transportation and centering ability of three single-file systems in severely curved canals using micro-computed tomography.Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2024 Feb 22;21:12. eCollection 2024. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2024. PMID: 38476716 Free PMC article.
-
Apical extrusion of debris after canal shaping with three single-file systems.Niger J Clin Pract. 2020 Jan;23(1):79-83. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_319_19. Niger J Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 31929211
-
Comparison of root canal shaping ability of different heat-treated NiTi single files: a micro-CT study.Quintessence Int. 2022 Jan 7;53(2):112-121. doi: 10.3290/j.qi.b2091311. Quintessence Int. 2022. PMID: 34595903 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Transportation and Centering Ability in Curved Mesiobuccal Canals of Mandibular First Molars after Instrumentation with Different File Systems-An In vitro Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023 Jul;15(Suppl 2):S1211-S1214. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_157_23. Epub 2023 Jul 11. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2023. PMID: 37694024 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Impact of using single-file reciprocating system on the quality of root canal treatment treated by undergraduate students.Saudi Dent J. 2024 Oct;36(10):1369-1375. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2024.08.011. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Saudi Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39525925 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the canal transportation of ProTaper GOLD, WaveOne GOLD, and TruNatomy in simulated double-curved canals.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Oct 16;21(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01854-z. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 34656099 Free PMC article.
-
Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Egyptian subpopulation: a cone-beam computed tomography study.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Apr 15;23(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02939-7. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37061674 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping ability of four single-file systems in the instrumentation of second mesiobuccal canals of three-dimensional printed maxillary first molars.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Sep;9(18):1425. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3855. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34733977 Free PMC article.
-
A microcomputed tomographic analysis of the morphological variabilities and incidence of extra canals in mandibular first molar teeth in an Egyptian subpopulation.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 2;13(1):8985. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-36005-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37268728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schilder H. Cleaning and shaping the root canal. Dent Clin North Am. 1974;18(02):269–296. - PubMed
-
- Hülsmann M, Peters O A, Dummer P M. Mechanical preparation of root canals: shaping goals, techniques and means. Endod Topics. 2005;10:30–76.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

