A Review of ULK1-Mediated Autophagy in Drug Resistance of Cancer
- PMID: 32033142
- PMCID: PMC7073181
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12020352
A Review of ULK1-Mediated Autophagy in Drug Resistance of Cancer
Abstract
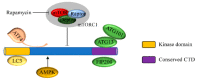
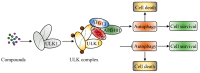
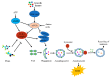
The difficulty of early diagnosis and the development of drug resistance are two major barriers to the successful treatment of cancer. Autophagy plays a crucial role in several cellular functions, and its dysregulation is associated with both tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Unc-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) is a serine/threonine kinase that participates in the initiation of autophagy. Many studies have indicated that compounds that directly or indirectly _target ULK1 could be used for tumor therapy. However, reports of the therapeutic effects of these compounds have come to conflicting conclusions. In this work, we reviewed recent studies related to the effects of ULK1 on the regulation of autophagy and the development of drug resistance in cancers, with the aim of clarifying the mechanistic underpinnings of this therapeutic _target.
Keywords: ULK1; autophagy; cancer; drug resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autophagy and beyond: Unraveling the complexity of UNC-51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) from biological functions to therapeutic implications.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Oct;12(10):3743-3782. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.06.004. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 36213540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of ULK1 Catalytic Activity and Its Regulation.Methods Enzymol. 2017;587:391-404. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.09.067. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28253968
-
ULK1 O-GlcNAcylation Is Crucial for Activating VPS34 via ATG14L during Autophagy Initiation.Cell Rep. 2018 Dec 4;25(10):2878-2890.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.11.042. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30517873
-
SBI0206965, a novel inhibitor of Ulk1, suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by modulating both autophagy and apoptosis pathways.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jun;37(6):3449-3458. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5635. Epub 2017 May 10. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28498429
-
Role of an intrinsically disordered conformation in AMPK-mediated phosphorylation of ULK1 and regulation of autophagy.Mol Biosyst. 2012 Jan;8(1):91-6. doi: 10.1039/c1mb05265a. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Mol Biosyst. 2012. PMID: 21853163 Review.
Cited by
-
The Roles of Post-Translational Modifications on mTOR Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1784. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041784. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy and apoptosis induction by sesamin in MOLT-4 and NB4 leukemia cells.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jan;21(1):32. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12293. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33262824 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy dictates sensitivity to PRMT5 inhibitor in breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 3;13(1):10752. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37706-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37400460 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in _targeting Cancer-Associated Genes by Designed siRNA in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 3;12(12):3619. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123619. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors for Unc-51-like Autophagy-Activating Kinase _targeting Autophagy in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 4;24(2):953. doi: 10.3390/ijms24020953. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

