A Retrospective Study of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for the Management of Diabetes After Transplantation
- PMID: 32072430
- PMCID: PMC7136376
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-020-00786-1
A Retrospective Study of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for the Management of Diabetes After Transplantation
Abstract
Introduction: Management of post-transplant diabetes mellitus is challenging; there is a lack of prospective randomized controlled trials for safety and efficacy of antidiabetic medications in solid organ recipients. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) are a relatively new class of medications used to manage type 2 diabetes in the general population. They have several benefits besides glycemic control, including weight loss and improved cardiovascular risk. However, they have not been studied extensively in the post-transplant population for safety and efficacy.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of patients who had received kidney, liver, or heart transplant, had diabetes either pre- or post-transplant, and were treated with GLP-1RA. We identified seven kidney, seven liver, and five heart transplant recipients who had received GLP-1RA. We assessed changes in immunosuppressant levels, rejection episodes, changes in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), weight, and body mass index (BMI) while on the GLP-1RA. We also looked at changes in insulin dose, other diabetes medications, heart rate, blood pressure, and renal function.
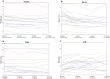
Results: After a mean follow-up period of 12 months, there were no significant changes in tacrolimus (FK506) levels and renal function for the period of GLP-1RA use. At the end of 12 months, the mean drop in weight was 4.86 kg [95% CI - 7.79, - 1.93]. The BMI decreased by a mean of 1.63 kg/m2 at the end of 12 months [95% CI - 2.53, - 0.73]. HbA1c decreased from baseline by 1.08% [95% CI - 1.65, - 0.51], 0.96% [95% CI - 1.68, - 0.25], and 0.75% [95% CI - 1.55, 0.05] at 3, 6, and 12 months, respectively.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that GLP-1RA do not affect tacrolimus levels or transplant outcomes in solid organ transplant (SOT) recipients in the short term. GLP-1RA also seem to be as effective in SOT recipients for glycemic control and weight loss as in the non-transplant population with diabetes.
Keywords: GLP-1RA; Glucose; Immunosuppressants; Transplant; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for diabetes after solid organ transplantation.Transpl Int. 2021 Aug;34(8):1341-1359. doi: 10.1111/tri.13883. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Transpl Int. 2021. PMID: 33880815 Review.
-
Glucagon-like-1 receptor agonists and sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors combination-are we exploiting their full potential in a real life setting?World J Diabetes. 2020 Nov 15;11(11):540-552. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v11.i11.540. World J Diabetes. 2020. PMID: 33269065 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020 Oct;22(10):1857-1868. doi: 10.1111/dom.14108. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020. PMID: 32476254
-
Management of Diabetes Mellitus in Normal Renal Function, Renal Dysfunction and Renal Transplant Recipients, Focusing on Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Agonist: A Review Based upon Current Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 28;20(13):3152. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133152. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors, and Their Combination on Endothelial Glycocalyx, Arterial Function, and Myocardial Work Index in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus After 12-Month Treatment.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 May 5;9(9):e015716. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015716. Epub 2020 Apr 24. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32326806 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Feb 2;17(2):sfae018. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae018. eCollection 2024 Feb. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 38410684 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 Agonism for Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence and Future Directions Across the Research Spectrum.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2024 Oct 31;11:20543581241290317. doi: 10.1177/20543581241290317. eCollection 2024. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39492845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 30;13(3):793. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030793. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International consensus on post-transplantation diabetes mellitus.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024 Feb 28;39(3):531-549. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad258. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38171510 Free PMC article.
-
Posttransplant complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 2;5(9):e669. doi: 10.1002/mco2.669. eCollection 2024 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39224537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources