Noncoding microRNAs: small RNAs play a big role in regulation of ADME?
- PMID: 32154096
- PMCID: PMC7061715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2012.02.011
Noncoding microRNAs: small RNAs play a big role in regulation of ADME?
Abstract
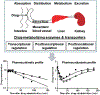
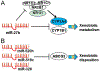
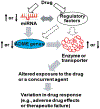
There are considerable interindividual variations in drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) in humans, which may lead to undesired drug effects in pharmacotherapy. Some of the mechanistic causes are known, e.g., genetic polymorphism, inhibition and induction of ADME enzymes and transporters, while others such as posttranscriptional regulation of ADME genes are under active study. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a large group of small, noncoding RNAs that control posttranscriptional expression of _target genes. More than 1000 miRNAs have been identified in the human genome, which may regulate thousands of protein-coding genes. Some miRNAs directly or indirectly control the expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome P450 enzymes, ATP-binding cassette or solute carrier transporters and/or nuclear receptors. Consequently, intervention of miRNA epigenetic signaling may alter ADME gene expression, change the capacity of drug metabolism and transport, and influence the sensitivity of cells to xenobiotics. In addition, the expression of some ADME regulatory miRNAs is significantly changed in cells following the exposure to a given drug, and the consequent changes in ADME gene expression might result in distinct ADME properties and drug response. In this review, we summarized recent findings on the role of noncoding miRNAs in epigenetic regulation of ADME genes and discussed the potential impact on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Keywords: Cancer; Epigenetics; Gene regulation; MicroRNA; Multidrug resistance; Pharmacokinetics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efflux ABC transporters in drug disposition and their posttranscriptional gene regulation by microRNAs.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1423416. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423416. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39114355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Novel Recombinant RNAs for Studying Post-transcriptional Gene Regulation in Drug Metabolism and Disposition.Curr Drug Metab. 2023;24(3):175-189. doi: 10.2174/1389200224666230425232433. Curr Drug Metab. 2023. PMID: 37170982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in the regulation of drug metabolism and disposition.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009 Dec;5(12):1513-28. doi: 10.1517/17425250903307448. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19785514 Review.
-
MicroRNAs as regulators of drug transporters, drug-metabolizing enzymes, and tight junctions: implication for intestinal barrier function.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Aug;143(2):217-24. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.03.002. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24631272 Review.
-
MicroRNA Pharmacoepigenetics: Posttranscriptional Regulation Mechanisms behind Variable Drug Disposition and Strategy to Develop More Effective Therapy.Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Mar;44(3):308-19. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.067470. Epub 2015 Nov 13. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016. PMID: 26566807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efflux ABC transporters in drug disposition and their posttranscriptional gene regulation by microRNAs.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 24;15:1423416. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423416. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39114355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miR-320a-3p and miR-483-5p level associated with pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic profiles of rivaroxaban.Hum Genomics. 2022 Dec 28;16(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s40246-022-00445-5. Hum Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36578040 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the Regulation of Solute Carrier Proteins Behind Xenobiotic and Nutrient Transport in Cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 9;9:893846. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.893846. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35755805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reducing Hepatocyte Injury and Necrosis in Response to Paracetamol Using Noncoding RNAs.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016 Jun;5(6):764-72. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0117. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27057006 Free PMC article.
-
Advances and challenges in studying noncoding RNA regulation of drug metabolism and development of RNA therapeutics.Biochem Pharmacol. 2019 Nov;169:113638. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113638. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31518552 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bennett CL, Nebeker JR, Lyons EA, Samore MH, Feldman MD, McKoy JM, et al. The research on adverse drug events and reports (RADAR) project. J Am Med Assoc 2005;293:2131–40. - PubMed
-
- Gurwitz JH, Field TS, Harrold LR, Rothschild J, Debellis K, Seger AC, et al. Incidence and preventability of adverse drug events among older persons in the ambulatory setting. J Am Med Assoc 2003;289:1107–16. - PubMed
-
- Haga SB, Thummel KE, Burke W. Adding pharmacogenetics information to drug labels: lessons learned. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2006;16:847–54. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
