Relationship Between Sleep and Behavior in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Exploring the Impact of Sleep Variability
- PMID: 32265629
- PMCID: PMC7105870
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00211
Relationship Between Sleep and Behavior in Autism Spectrum Disorder: Exploring the Impact of Sleep Variability
Abstract
Objective: The relationship between sleep (caregiver-reported and actigraphy-measured) and other caregiver-reported behaviors in children and adults with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) was examined, including the use of machine learning to identify sleep variables important in predicting anxiety in ASD.
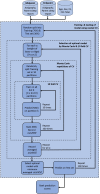
Methods: Caregivers of ASD (n = 144) and typically developing (TD) (n = 41) participants reported on sleep and other behaviors. ASD participants wore an actigraphy device at nighttime during an 8 or 10-week non-interventional study. Mean and variability of actigraphy measures for ASD participants in the week preceding midpoint and endpoint were calculated and compared with caregiver-reported and clinician-reported symptoms using a mixed effects model. An elastic-net model was developed to examine which sleep measures may drive prediction of anxiety.
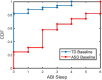
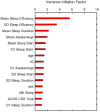
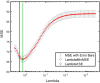
Results: Prevalence of caregiver-reported sleep difficulties in ASD was approximately 70% and correlated significantly (p < 0.05) with sleep efficiency measured by actigraphy. Mean and variability of actigraphy measures like sleep efficiency and number of awakenings were related significantly (p < 0.05) to ASD symptom severity, hyperactivity and anxiety. In the elastic net model, caregiver-reported sleep, and variability of sleep efficiency and awakenings were amongst the important predictors of anxiety.
Conclusion: Caregivers report problems with sleep in the majority of children and adults with ASD. Reported problems and actigraphy measures of sleep, particularly variability, are related to parent reported behaviors. Measuring variability in sleep may prove useful in understanding the relationship between sleep problems and behavior in individuals with ASD. These findings may have implications for both intervention and monitoring outcomes in ASD.
Keywords: ASD; actigraphy; anxiety; hyperactivity; irritability; sleep; variability.
Copyright © 2020 Bangerter, Chatterjee, Manyakov, Ness, Lewin, Skalkin, Boice, Goodwin, Dawson, Hendren, Leventhal, Shic, Esbensen and Pandina.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sleep behaviors and sleep quality in children with autism spectrum disorders.Sleep. 2009 Dec;32(12):1566-78. doi: 10.1093/sleep/32.12.1566. Sleep. 2009. PMID: 20041592 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Relationship of Sleep Disturbances to Severity and Common Behaviors in Autism Spectrum Disorder.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 23:rs.3.rs-2674526. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2674526/v1. Res Sq. 2023. PMID: 36993672 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Sleep disturbances and physical health problems in caregivers of children with ASD.Res Dev Disabil. 2021 Jun;113:103932. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2021.103932. Epub 2021 Mar 14. Res Dev Disabil. 2021. PMID: 33730686
-
Assessment of Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Children (Basel). 2017 Aug 8;4(8):72. doi: 10.3390/children4080072. Children (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28786962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep Disorders in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder: Insights From Animal Models, Especially Non-human Primate Model.Front Behav Neurosci. 2021 May 20;15:673372. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2021.673372. eCollection 2021. Front Behav Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34093147 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complexity of Body Movements during Sleep in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Entropy (Basel). 2021 Mar 31;23(4):418. doi: 10.3390/e23040418. Entropy (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807381 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbances of Continuous Sleep and Circadian Rhythms Account for Behavioral Difficulties in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.J Clin Med. 2020 Jun 24;9(6):1978. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061978. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32599848 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Bidirectional Relationships: Child Sleep Duration, Child Behavior Problems, and Parenting Stress in Families of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder.Res Autism Spectr Disord. 2023 Aug;106:102197. doi: 10.1016/j.rasd.2023.102197. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Res Autism Spectr Disord. 2023. PMID: 37484880 Free PMC article.
-
Severity of Autism Spectrum Disorder Symptoms Associated with de novo Variants and Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension.J Autism Dev Disord. 2024 Feb;54(2):749-764. doi: 10.1007/s10803-022-05824-4. Epub 2022 Nov 29. J Autism Dev Disord. 2024. PMID: 36445517
-
Assessing fatigue and sleep in chronic diseases using physiological signals from wearables: A pilot study.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 14;13:968185. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.968185. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36452041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams H. L., Matson J. L., Cervantes P. E., Goldin R. L. (2014a). The relationship between autism symptom severity and sleep problems: should bidirectionality be considered? Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 8 193–199. 10.1016/j.rasd.2013.11.008 - DOI
-
- Adams H. L., Matson J. L., Jang J. (2014b). The relationship between sleep problems and challenging behavior among children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 8 1024–1030. 10.1016/j.rasd.2014.05.008 - DOI
-
- Aman M. G., Singh N. N. (2017). Aberrant Behavior Checklist Manual, 2nd Edn East Aurora, NY: Slosson Educational Publications, Inc.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

