Osteocyte-Related Cytokines Regulate Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption
- PMID: 32708317
- PMCID: PMC7404053
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21145169
Osteocyte-Related Cytokines Regulate Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption
Abstract
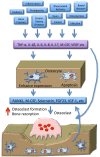
The process of bone remodeling is the result of the regulated balance between bone cell populations, namely bone-forming osteoblasts, bone-resorbing osteoclasts, and the osteocyte, the mechanosensory cell type. Osteoclasts derived from the hematopoietic stem cell lineage are the principal cells involved in bone resorption. In osteolytic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, periodontitis, and osteoporosis, the balance is lost and changes in favor of bone resorption. Therefore, it is vital to elucidate the mechanisms of osteoclast formation and bone resorption. It has been reported that osteocytes express Receptor activator of nuclear factor κΒ ligand (RANKL), an essential factor for osteoclast formation. RANKL secreted by osteocytes is the most important factor for physiologically supported osteoclast formation in the developing skeleton and in pathological bone resorption such as experimental periodontal bone loss. TNF-α directly enhances RANKL expression in osteocytes and promotes osteoclast formation. Moreover, TNF-α enhances sclerostin expression in osteocytes, which also increases osteoclast formation. These findings suggest that osteocyte-related cytokines act directly to enhance osteoclast formation and bone resorption. In this review, we outline the most recent knowledge concerning bone resorption-related cytokines and discuss the osteocyte as the master regulator of bone resorption and effector in osteoclast formation.
Keywords: bone; cytokine; osteoclast; osteocyte.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scl-Ab reverts pro-osteoclastogenic signalling and resorption in estrogen deficient osteocytes.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Nov 4;21(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12860-020-00322-w. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 33148174 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of TNF-α-Induced Sclerostin on Osteocytes during Orthodontic Tooth Movement.J Immunol Res. 2019 Jun 24;2019:9716758. doi: 10.1155/2019/9716758. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31341915 Free PMC article.
-
Osteocyte RANKL Drives Bone Resorption in Mouse Ligature-Induced Periodontitis.J Bone Miner Res. 2023 Oct;38(10):1521-1540. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.4897. Epub 2023 Aug 23. J Bone Miner Res. 2023. PMID: 37551879 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways.J Bone Miner Metab. 2021 Jan;39(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00774-020-01162-6. Epub 2020 Oct 20. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021. PMID: 33079279 Review.
-
Osteocyte-Mediated Translation of Mechanical Stimuli to Cellular Signaling and Its Role in Bone and Non-bone-Related Clinical Complications.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020 Feb;18(1):67-80. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00564-9. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020. PMID: 31953640 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Different Types of Cannabinoids in Periodontal Disease: An Integrative Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 4;16(7):893. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070893. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights into nanotherapeutics for periodontitis: a triple concerto of antimicrobial activity, immunomodulation and periodontium regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jan 4;22(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02261-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38178140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the Interaction of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors 1 and 2 in Bone-Related Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 27;23(3):1481. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031481. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Osteocyte Stimulated by Wnt Agonist SKL2001 Is a Safe Osteogenic Niche Improving Bioactivities in a Polycaprolactone and Cell Integrated 3D Module.Cells. 2022 Feb 28;11(5):831. doi: 10.3390/cells11050831. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269452 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Osteoporotic Effect of Morroniside on Osteoblast and Osteoclast Differentiation In Vitro and Ovariectomized Mice In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 30;22(19):10642. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910642. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638983 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

