Activation of Toll-like receptor 5 in microglia modulates their function and triggers neuronal injury
- PMID: 32912327
- PMCID: PMC7488138
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-020-01031-3
Activation of Toll-like receptor 5 in microglia modulates their function and triggers neuronal injury
Abstract
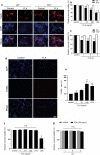
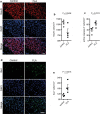
Microglia are the primary immune-competent cells of the central nervous system (CNS) and sense both pathogen- and host-derived factors through several receptor systems including the Toll-like receptor (TLR) family. Although TLR5 has previously been implicated in different CNS disorders including neurodegenerative diseases, its mode of action in the brain remained largely unexplored. We sought to determine the expression and functional consequences of TLR5 activation in the CNS. Quantitative real-time PCR and immunocytochemical analysis revealed that microglia is the major CNS cell type that constitutively expresses TLR5. Using Tlr5-/- mice and inhibitory TLR5 antibody we found that activation of TLR5 in microglial cells by its agonist flagellin, a principal protein component of bacterial flagella, triggers their release of distinct inflammatory molecules, regulates chemotaxis, and increases their phagocytic activity. Furthermore, while TLR5 activation does not affect tumor growth in an ex vivo GL261 glioma mouse model, it triggers microglial accumulation and neuronal apoptosis in the cerebral cortex in vivo. TLR5-mediated microglial function involves the PI3K/Akt/mammalian _target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway, as specific inhibitors of this signaling pathway abolish microglial activation. Taken together, our findings establish TLR5 as a modulator of microglial function and indicate its contribution to inflammatory and injurious processes in the CNS.
Keywords: Chemotaxis; Cytokines; Microglia; Neuronal apoptosis; PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 signaling; Phagocytosis; Toll-like receptor 5.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Necrotic neurons enhance microglial neurotoxicity through induction of glutaminase by a MyD88-dependent pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2008 Oct 9;5:43. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-5-43. J Neuroinflammation. 2008. PMID: 18844999 Free PMC article.
-
TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) activation suppresses autophagy through inhibition of FOXO3 and impairs phagocytic capacity of microglia.Autophagy. 2019 May;15(5):753-770. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1556946. Epub 2018 Dec 13. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30523761 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 5-mediated signaling enhances liver regeneration in mice.Mil Med Res. 2021 Feb 23;8(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40779-021-00309-4. Mil Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33622404 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the CNS: the role of microglia in Toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury.Glia. 2010 Feb;58(3):253-63. doi: 10.1002/glia.20928. Glia. 2010. PMID: 19705460 Review.
-
Neuronal influence behind the central nervous system regulation of the immune cells.Front Integr Neurosci. 2013 Sep 2;7:64. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2013.00064. Front Integr Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24032006 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Host immune responses in the central nervous system during fungal infections.Immunol Rev. 2022 Oct;311(1):50-74. doi: 10.1111/imr.13101. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Immunol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35672656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toll-like receptor-mediated neuroinflammation: relevance for cognitive dysfunctions.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Sep;43(9):726-739. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35753845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Supervised latent factor modeling isolates cell-type-specific transcriptomic modules that underlie Alzheimer's disease progression.Commun Biol. 2024 May 17;7(1):591. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06273-8. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38760483 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Cortical Cell Tri-Culture-Based Screening of Neuroinflammatory Response in Toll-like Receptor Activation.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 29;10(9):2122. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092122. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140221 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptors and toll-like receptor-_targeted immunotherapy against glioma.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Oct 29;14(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01191-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34715891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buonfiglioli A, Efe IE, Guneykaya D, Ivanov A, Huang Y, Orlowski E, Kruger C, Deisz RA, Markovic D, Fluh C, et al. let-7 microRNAs regulate microglial function and suppress glioma growth through Toll-Like Receptor 7. Cell Rep. 2019;29(3460–3471):e3467. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.11.029. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

