ACSS2-related autophagy has a dual impact on memory
- PMID: 32922914
- PMCID: PMC7398205
- DOI: 10.1186/s41016-019-0162-y
ACSS2-related autophagy has a dual impact on memory
Abstract
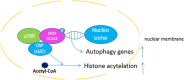
Autophagy is an intracellular degenerative pathway which is responsible for neuronal survival. Under the condition of nutrient deprivation, autophagy can lead to dysfunction in memory consolidation. AMPK/mTOR pathway is currently the most studied autophagy mechanism, while recently researchers have proved ACSS2 can also affect autophagy. ACSS2 is phosphorylated at Ser659 by AMPK and then forms a translocation complex with Importin α5 to translocate into the nucleus. This process interacts with TFEB, resulting in upregulated expression of lysosomal and autophagosomal genes. These upregulations inhibit synaptic plasticity and hence memory functions. On the other hand, ACSS2 is also recognized as a regulator of histone acetylation. After recruiting CBP/p300 and activating CBP's HAT activity in the nucleus, ACSS2 maintains the level of localized histone acetylation by recapturing acetate from histone deacetylation to reform acetyl-CoA, providing substrates for HAT. The increase of histone acetylation locally enhanced immediate early gene transcription, including Egr2, Fos, Nr2f2, Sgk1, and Arc, to benefit neuronal plasticity and memory in many ways.
Keywords: ACSS2; Histone acetylation; Memory; TFEB.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Local histone acetylation by ACSS2 promotes gene transcription for lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy.Autophagy. 2017 Oct 3;13(10):1790-1791. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1349581. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Autophagy. 2017. PMID: 28820290 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleus-Translocated ACSS2 Promotes Gene Transcription for Lysosomal Biogenesis and Autophagy.Mol Cell. 2017 Jun 1;66(5):684-697.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.04.026. Epub 2017 May 25. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28552616 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-CoA Metabolism and Histone Acetylation in the Regulation of Aging and Lifespan.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Apr 8;10(4):572. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040572. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acetyl-CoA synthetase regulates histone acetylation and hippocampal memory.Nature. 2017 Jun 15;546(7658):381-386. doi: 10.1038/nature22405. Epub 2017 May 31. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28562591 Free PMC article.
-
Acetyl-CoA synthetase 2(ACSS2): a review with a focus on metabolism and tumor development.Discov Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;13(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00521-1. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35798917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Image-guided metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal tumour heterogeneity in luminal A and B human breast cancer beyond glucose tracer uptake.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Feb;14(2):e1550. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1550. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38332687 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
