Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment
- PMID: 32959892
- PMCID: PMC7536980
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.30055
Quantitative proteomics reveals a broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin, benefiting for COVID-19 treatment
Abstract
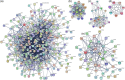
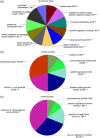
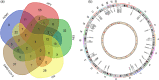
Viruses such as human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), human papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 [SARS-CoV-2]) represent a great burden to human health worldwide. FDA-approved anti-parasite drug ivermectin is also an antibacterial, antiviral, and anticancer agent, which offers more potentiality to improve global public health, and it can effectively inhibit the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. This study sought to identify ivermectin-related virus infection pathway alterations in human ovarian cancer cells. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) quantitative proteomics was used to analyze human ovarian cancer cells TOV-21G treated with and without ivermectin (20 μmol/L) for 24 h, which identified 4447 ivermectin-related proteins in ovarian cancer cells. Pathway network analysis revealed four statistically significant antiviral pathways, including HCMV, HPV, EBV, and HIV1 infection pathways. Interestingly, compared with the reported 284 SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19-related genes from GencLip3, we identified 52 SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19-related protein alterations when treated with and without ivermectin. Protein-protein network (PPI) was constructed based on the interactions between 284 SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19-related genes and between 52 SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19-related proteins regulated by ivermectin. Molecular complex detection analysis of PPI network identified three hub modules, including cytokines and growth factor family, MAP kinase and G-protein family, and HLA class proteins. Gene Ontology analysis revealed 10 statistically significant cellular components, 13 molecular functions, and 11 biological processes. These findings demonstrate the broad-spectrum antiviral property of ivermectin benefiting for COVID-19 treatment in the context of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine in virus-related diseases.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19; ivermectin; quantitative proteomics; stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture; virus-related pathways.
© 2020 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SILAC quantitative proteomics analysis of ivermectin-related proteomic profiling and molecular network alterations in human ovarian cancer cells.J Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan;56(1):e4659. doi: 10.1002/jms.4659. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33047383
-
The broad spectrum host-directed agent ivermectin as an antiviral for SARS-CoV-2 ?Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.042. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33341233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ivermectin as a Broad-Spectrum Host-Directed Antiviral: The Real Deal?Cells. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):2100. doi: 10.3390/cells9092100. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32942671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moxidectin and Ivermectin Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Vero E6 Cells but Not in Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Jan 18;66(1):e0154321. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01543-21. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34633839 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomics revealed energy metabolism pathway alterations in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma and their regulation by the antiparasite drug ivermectin: data interpretation in the context of 3P medicine.EPMA J. 2020 Oct 10;11(4):661-694. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00224-z. eCollection 2020 Dec. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 33240452 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Proteomics advances towards developing SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics using in silico drug repurposing approaches.Drug Discov Today Technol. 2021 Dec;39:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ddtec.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2021. PMID: 34906319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ivermectin Prophylaxis Used for COVID-19: A Citywide, Prospective, Observational Study of 223,128 Subjects Using Propensity Score Matching.Cureus. 2022 Jan 15;14(1):e21272. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21272. eCollection 2022 Jan. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35070575 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 inhibitors as a treatment for melanoma: Promising agents against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Dermatol Ther. 2020 Nov;33(6):e14449. doi: 10.1111/dth.14449. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Dermatol Ther. 2020. PMID: 33098610 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Antiparasitic Drugs against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Literature Survey.Microorganisms. 2022 Jun 24;10(7):1284. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071284. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regular Use of Ivermectin as Prophylaxis for COVID-19 Led Up to a 92% Reduction in COVID-19 Mortality Rate in a Dose-Response Manner: Results of a Prospective Observational Study of a Strictly Controlled Population of 88,012 Subjects.Cureus. 2022 Aug 31;14(8):e28624. doi: 10.7759/cureus.28624. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36196304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdeltawab, M. S. A. , Rifaie, S. A. , Shoeib, E. Y. , El‐Latif, H. A. A. , Badawi, M. , Salama, W. H. , & El‐Aal, A. A. A. (2020). Insights into the impact of Ivermectin on some protein aspects linked to Culex pipiens digestion and immunity. Parasitology Research, 119(1), 55–62. - PubMed
-
- Almeida, A. M. , Queiroz, J. A. , Sousa, F. , & Sousa, Â. (2019). Cervical cancer and HPV infection: Ongoing therapeutic research to counteract the action of E6 and E7 oncoproteins. Drug Discovery Today, 24(10), 2044–2057. - PubMed
-
- Andoniou, C. E. , & Degli‐Esposti, M. A. (2006). Insights into the mechanisms of CMV‐mediated interference with cellular apoptosis. Immunology and Cell Biology, 84(1), 99–106. - PubMed
-
- Ashour, D. S. (2019). Ivermectin: From theory to clinical application. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents, 54(2), 134–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

