Identification and characterization of a novel adiponectin receptor agonist adipo anti-inflammation agonist and its anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 32986862
- PMCID: PMC8364772
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15277
Identification and characterization of a novel adiponectin receptor agonist adipo anti-inflammation agonist and its anti-inflammatory effects in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background and purpose: Adiponectin (APN) is an adipokine secreted from adipocytes that binds to APN receptors AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 and exerts an anti-inflammatory response through mechanisms not fully understood. There is a need to develop small molecules that activate AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 and to be used to inhibit the inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemia and other inflammatory disorders.
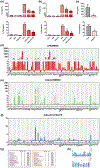
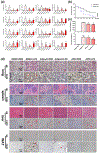
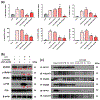
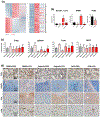
Experimental approach: We designed 10 new structural analogues of an AdipoR agonist, AdipoRon (APR), and assessed their anti-inflammatory properties. Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMMs) and peritoneal macrophages (PEMs) were isolated from mice. Levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines were measured by reverse transcription and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and microarray in LPS-induced endotoxemia mice and diet-induced obesity (DIO) mice in which systemic inflammation prevails. Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), siRNA interference and immunoprecipitation were used to detect signalling pathways.
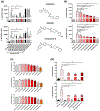
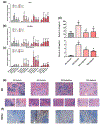
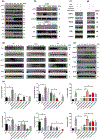
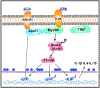
Key results: A novel APN receptor agonist named adipo anti-inflammation agonist (AdipoAI) strongly suppresses inflammation in DIO and endotoxemia mice, as well as in cultured macrophages. We also found that AdipoAI attenuated the association of AdipoR1 and APPL1 via myeloid differentiation marker 88 (MyD88) signalling, thus inhibiting activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and c-Maf pathways and limiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in LPS-induced macrophages.
Conclusion and implications: AdipoAI is a promising alternative therapeutic approach to APN and APR to suppress inflammation in LPS-induced endotoxemia and other inflammatory disorders via distinct signalling pathways.
Keywords: APPL1; AdipoAI; MyD88; c-Maf; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide.
© 2020 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest concerning the authorship or publication of this article. All authors have followed the recommendations set out in the
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel adiponectin receptor agonist (AdipoAI) ameliorates type 2 diabetes-associated periodontitis by enhancing autophagy in osteoclasts.J Periodontal Res. 2022 Apr;57(2):381-391. doi: 10.1111/jre.12969. Epub 2022 Jan 4. J Periodontal Res. 2022. PMID: 34984683 Free PMC article.
-
The adiponectin receptor agonist AdipoAI attenuates periodontitis in diabetic rats by inhibiting gingival fibroblast-induced macrophage migration.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Sep;180(18):2436-2451. doi: 10.1111/bph.16103. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37143319
-
Adiponectin-AdipoR1/2-APPL1 signaling axis suppresses human foam cell formation: differential ability of AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 to regulate inflammatory cytokine responses.Atherosclerosis. 2012 Mar;221(1):66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.12.014. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Atherosclerosis. 2012. PMID: 22227293 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin-Resistance in Obesity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:415-441. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_18. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28585210 Review.
-
Pharmacological _targeting of adaptor proteins in chronic inflammation.Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct;73(10):1645-1656. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01921-5. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39052063 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a non-invasive bioassay for adiponectin _target engagement in mice.iScience. 2024 Sep 19;27(10):110994. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110994. eCollection 2024 Oct 18. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39435143 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA APDC plays important regulatory roles in metabolism of bone and adipose tissues.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):836-846. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2268489. Epub 2023 Nov 13. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37953645 Free PMC article.
-
AdipoRon and Other Adiponectin Receptor Agonists as Potential Candidates in Cancer Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 25;22(11):5569. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115569. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel adiponectin receptor agonist (AdipoAI) ameliorates type 2 diabetes-associated periodontitis by enhancing autophagy in osteoclasts.J Periodontal Res. 2022 Apr;57(2):381-391. doi: 10.1111/jre.12969. Epub 2022 Jan 4. J Periodontal Res. 2022. PMID: 34984683 Free PMC article.
-
The Periodontal Pathogen Fusobacterium nucleatum Exacerbates Alzheimer's Pathogenesis via Specific Pathways.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jun 23;14:912709. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.912709. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35813949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander SPH, Roberts RE, Broughton BRS, Sobey CG, George CH, Stanford SC, … Ahluwalia A, (2018). Goals and practicalities of immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry: A guide for submission to the British Journal of Pharmacology. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175, 407–411. 10.1111/bph.14112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van den Bosch MW, Palsson-Mcdermott E, Johnson DS, & O’Neill LA, (2014). LPS induces the degradation of programmed cell death protein 4 (PDCD4) to release Twist2, activating c-Maf transcription to promote interleukin-10 production. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(33), 22980–22990. 10.1074/jbc.M114.573089 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

