Impact of overproduced heterologous protein characteristics on physiological response in Yarrowia lipolytica steady-state-maintained continuous cultures
- PMID: 33025130
- PMCID: PMC7595971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-020-10937-w
Impact of overproduced heterologous protein characteristics on physiological response in Yarrowia lipolytica steady-state-maintained continuous cultures
Abstract
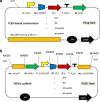
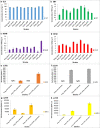
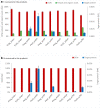
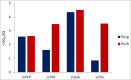
Overproduction of recombinant secretory proteins triggers numerous physiological perturbations. Depending on a given heterologous protein characteristics, the producer cell is faced with different challenges which lead to varying responses in terms of its physiology and the _target protein production rate. In the present study, we used steady-state-maintained Yarrowia lipolytica cells to investigate the impact of different heterologous proteins on the physiological behavior of the host cells. Such an approach allowed to uncouple the impact of the overproduction of a particular protein from the phenomena that result from growth phase or are caused by the heterogeneity of the analyzed populations. Altogether, eight variants of recombinant strains, individually overproducing heterologous proteins of varying molecular weight (27-65 kDa) and reporting activity (enzymatic and fluorescent) were subjected to chemostat cultivations. The steady-state-maintained cells were analyzed in terms of the substrate utilization, biomass and metabolites production, as well as the reporter protein synthesis. Simplified distribution of carbon and nitrogen between the respective products, as well as expression analysis of the heterologous genes were conducted. The here-obtained data suggest that using a more transcriptionally active promoter results in channeling more C flux towards the _target protein, giving significantly higher specific amounts and production rates of the _target polypeptide, at the cost of biomass accumulation, and with no significant impact on the polyols production. The extent of the reporter protein's post-translational modifications, i.e., the number of disulfide bonds and glycosylation pattern, strongly impacts the synthesis process. Specific responses in terms of the protein formation kinetics, the gene expression levels, and transcript-to-protein linearity were observed.Key Points• Eight expression systems, producing different reporter proteins were analyzed.• The cells were maintained in steady-state by continuous chemostat culturing.• Protein- and promoter-specific effects were observed.
Keywords: Chemostat; Heterologous protein; Overexpression; Overproduction; Recombinant strain; Secretion; Steady state.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interestsEthics approval
N/A
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis of Secretory Proteins in Yarrowia lipolytica: Effect of Combined Stress Factors and Metabolic Load.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 25;23(7):3602. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073602. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408958 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of oxygen availability on heterologous geneexpression and polypeptide secretion dynamics in Yarrowia lipolytica-based protein production platforms.Yeast. 2020 Sep;37(9-10):559-568. doi: 10.1002/yea.3499. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Yeast. 2020. PMID: 32445214
-
Heterologous protein expression and secretion in the non-conventional yeast Yarrowia lipolytica: a review.J Biotechnol. 2004 Apr 8;109(1-2):63-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2003.10.027. J Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15063615 Review.
-
Deciphering how LIP2 and POX2 promoters can optimally regulate recombinant protein production in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica.Microb Cell Fact. 2016 Sep 20;15(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0558-8. Microb Cell Fact. 2016. PMID: 27651221 Free PMC article.
-
Yarrowia lipolytica: recent achievements in heterologous protein expression and pathway engineering.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;99(11):4559-77. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6624-z. Epub 2015 May 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25947247 Review.
Cited by
-
An Interplay between Transcription Factors and Recombinant Protein Synthesis in Yarrowia lipolytica at Transcriptional and Functional Levels-The Global View.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9450. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179450. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273402 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Secretory Proteins in Yarrowia lipolytica: Effect of Combined Stress Factors and Metabolic Load.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 25;23(7):3602. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073602. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408958 Free PMC article.
-
Using Euf1 transcription factor as a titrator of erythritol-inducible promoters in Yarrowia lipolytica; insight into the structure, splicing, and regulation mechanism.FEMS Yeast Res. 2024 Jan 9;24:foae027. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foae027. FEMS Yeast Res. 2024. PMID: 39169472 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperosmolarity adversely impacts recombinant protein synthesis by Yarrowia lipolytica-molecular background revealed by quantitative proteomics.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jan;106(1):349-367. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11731-y. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34913994 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal treatment improves a process of crude glycerol valorization for the production of a heterologous enzyme by Yarrowia lipolytica.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021 Jun 19;31:e00648. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00648. eCollection 2021 Sep. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34221911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker JE, Woo SM (1985) Purification, partial characterization, and postembryonic levels of amylases from Sitophilus oryzae and Sitophilus granarius. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 2:415–428. 10.1002/arch.940020409
-
- Barth G, Gaillardin C. Yarrowia lipolytica. In: Wolf K, editor. Nonconventional yeasts in biotechnology: a handbook. Berlin: Springer; 1996. pp. 313–388.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

