Study protocol for the PURSUIT-HFpEF study: a Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
- PMID: 33060085
- PMCID: PMC7566724
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038294
Study protocol for the PURSUIT-HFpEF study: a Prospective, Multicenter, Observational Study of Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract
Introduction: Neither the pathophysiology nor an effective treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) has been elucidated to date. The purpose of this ongoing study is to elucidate the pathophysiology and prognostic factors for patients with HFpEF admitted to participating institutes. We also aim to obtain insights into the development of new diagnostic and treatment methods by analysing patient background factors, clinical data and follow-up information.
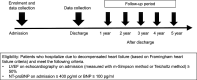
Methods and analysis: This study is a prospective, multicentre, observational study of patients aged ≥20 years admitted due to acute decompensated heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (≥50%) and elevated N-terminal-pro brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) (≥400 pg/mL). The study began in June 2016, with the participation of Osaka University Hospital and 31 affiliated facilities. We will collect data on history in detail, accompanying diseases, quality of life, frailty score, medication history, and laboratory and echocardiographic data. We will follow-up each patient for 5 years, and collect outcome data on mortality, cause of death, and the number and cause of hospitalisation. The _target number of registered cases is 1500 cases in 5 years.
Ethics and dissemination: The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Osaka University Hospital on 24 February 2016 (ID: 15471), and by the IRBs of the all participating facilities. The findings will be disseminated through peer-reviewed publications and conference presentations.
Keywords: cardiac epidemiology; cardiology; heart failure.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SS has received personal fees from Nihon Medi-Physics and FUJIFILM Toyama Chemical. SH has received personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo Company, Bayer, Astellas Pharma, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals and Boehringer Ingelheim Japan, and grants from Roche Diagnostics, FUJIFILM Toyama Chemical and Actelion Pharmaceuticals. AN has received personal fees from AstraZeneca and Otsuka Pharmaceutical. YM has a leadership position and stock of MKS, and has received a grant from MKS. HM has received personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo Company, Kowa Company, Bayer and Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, and a grant from Terumo. DN has received a personal fee from Daiichi Sankyo Company. YS has received personal fees from Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Ono Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation and Actelion Pharmaceuticals, and grants from Roche Diagnostic, FUJIFILM Toyama Chemical, Abbott Medical Japan, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation and Biotronik.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of the HFA-PEFF score in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Jun;8(3):2154-2164. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13302. Epub 2021 Mar 24. ESC Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 33760383 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and prognosis of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and elevated N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide: a 10-year analysis from the Copenhagen Hospital Heart Failure Study.Eur J Heart Fail. 2012 Mar;14(3):240-7. doi: 10.1093/eurjhf/hfs003. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012. PMID: 22315457
-
Modified Glasgow Prognostic Score is a novel predictor of clinical outcome in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.Scand Cardiovasc J. 2020 Jun;54(3):174-178. doi: 10.1080/14017431.2019.1709656. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2020. PMID: 31965867
-
Prognosis and NT-proBNP in heart failure patients with preserved versus reduced ejection fraction.Heart. 2019 Aug;105(15):1182-1189. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-314173. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Heart. 2019. PMID: 30962192 Free PMC article.
-
Is cardiac resynchronization therapy an option in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction? Justification for the ongoing KaRen project.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2010 Jun-Jul;103(6-7):404-10. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2010.01.009. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2010. PMID: 20800804 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Impact of Echocardiographic Congestion Grade in HFpEF With and Without Atrial Fibrillation.JACC Asia. 2022 Jan 18;2(1):73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jacasi.2021.10.012. eCollection 2022 Feb. JACC Asia. 2022. PMID: 36340256 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Sex in Left Atrial Indices for Prognosis of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 7;11(19):5910. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195910. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233777 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive prognostic factor of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction stratified with admission blood pressure.ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Aug;8(4):3145-3155. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13420. Epub 2021 May 16. ESC Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 33998166 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical relevance of quality of life in heart failure patients with preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Apr;10(2):995-1002. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14270. Epub 2022 Dec 12. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 36510693 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of interleukin-16 with different phenogroups in acute heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Aug;11(4):2354-2365. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14808. Epub 2024 Apr 30. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38686566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernandez AF, Hammill BG, O'Connor CM, et al. . Clinical effectiveness of beta-blockers in heart failure: findings from the OPTIMIZE-HF (organized program to initiate lifesaving treatment in hospitalized patients with heart failure) registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:184–92. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.09.031 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials