Effects of salt concentration, pH, and their interaction on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and photochemistry of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) leaves
- PMID: 33073686
- PMCID: PMC7671061
- DOI: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1832373
Effects of salt concentration, pH, and their interaction on plant growth, nutrient uptake, and photochemistry of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) leaves
Abstract
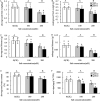
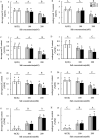
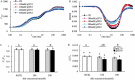
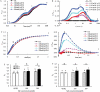
In order to explore the main limiting factors affecting the growth and physiological function of alfalfa under salt and alkali stress, the effect of the salt and alkali stress on the growth and physiological function of alfalfa was studied. The results showed that effects of the excessive salt concentration (100 and 200 mM) on the growth and physiological characteristics were significantly greater than that of pH (7.0 and 9.0). Under 100 mM salt stress, there was no significant difference in the growth and photosynthetic function between pH 9.0 and pH 7.0. Under the 200 mM salt concentration the absorption of Na+ by alfalfa treated at the pH 9.0 did not increase significantly compared with absorption at the pH 7.0. However, the higher pH directly reduced the root activity, leaf's water content, and N-P-K content also decreased significantly. The PSII and PSI activities decreased with increasing the salt concentration, especially the damage degree of PSI. Although the photoinhibition of PSII was not significant, PSII donor and electron transfer from the QA to QB of the PSII receptor sides was inhibited. In a word, alfalfa showed relatively strong salt tolerance capacity, at the 100 mM salt concentration, even when the pH reached 9.0. Thus, the effect on the growth and photosynthetic function was not significant. However, at 200 mM salt concentration, pH 9.0 treatment caused damage to root system and the photosynthetic function in leaves of alfalfa was seriously injured.
Keywords: Salt and alkali stress; alfalfa; photochemistry activity; photoinhibition; plant growth.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physiological and comparative transcriptome analysis of leaf response and physiological adaption to saline alkali stress across pH values in alfalfa (Medicago sativa).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Oct;167:140-152. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.07.040. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34352517
-
Characterization of physiological responses of two alfalfa half-sib families with improved salt tolerance.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013 Oct;71:103-11. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.06.026. Epub 2013 Jul 13. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23911728
-
Comparative analysis of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) leaf transcriptomes reveals genotype-specific salt tolerance mechanisms.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Feb 15;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1250-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29448940 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of non-uniform root zone salinity on growth, ion regulation, and antioxidant defense system in two alfalfa cultivars.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Nov;132:434-444. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.09.028. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30290335
-
Eco-physiological characteristics of alfalfa seedlings in response to various mixed salt-alkaline stresses.J Integr Plant Biol. 2008 Jan;50(1):29-39. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2007.00607.x. J Integr Plant Biol. 2008. PMID: 18666949
Cited by
-
Effect of salt-alkali stress on seed germination of the halophyte Halostachys caspica.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 8;14(1):13199. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61737-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38851793 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing quinoa growth under severe saline-alkali stress by phosphate solubilizing microorganism Penicillium funicuiosum P1.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 6;17(9):e0273459. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273459. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36067185 Free PMC article.
-
New Insight into Plant Saline-Alkali Tolerance Mechanisms and Application to Breeding.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 16;23(24):16048. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416048. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SbCASP4 improves salt exclusion by enhancing the root apoplastic barrier.Planta. 2021 Sep 23;254(4):81. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03731-z. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34554320
-
Integrated Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Rice Leaves Response to High Saline-Alkali Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 17;24(4):4062. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044062. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835473 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yan SH, Ji J, Wang G.. Effects of salt stress on plants and the mechanism of salt tolerance. World Sci-Technol Res Dev. 2006;28:70–76.
-
- Forni C, Duca D, Glick BR.. Mechanisms of plant response to salt and drought stress and their alteration by rhizobacteria. Plant Soil. 2017;410(1–2):335–356. doi:10.1007/s11104-016-3007-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
