Quantitative proteomics revealed energy metabolism pathway alterations in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma and their regulation by the antiparasite drug ivermectin: data interpretation in the context of 3P medicine
- PMID: 33240452
- PMCID: PMC7680500
- DOI: 10.1007/s13167-020-00224-z
Quantitative proteomics revealed energy metabolism pathway alterations in human epithelial ovarian carcinoma and their regulation by the antiparasite drug ivermectin: data interpretation in the context of 3P medicine
Abstract
Objective: Energy metabolism abnormality is the hallmark in epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC). This study aimed to investigate energy metabolism pathway alterations and their regulation by the antiparasite drug ivermectin in EOC for the discovery of energy metabolism pathway-based molecular biomarker pattern and therapeutic _targets in the context of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine (PPPM) in EOC.
Methods: iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics was used to identify mitochondrial differentially expressed proteins (mtDEPs) between human EOC and control mitochondrial samples isolated from 8 EOC and 11 control ovary tissues from gynecologic surgery of Chinese patients, respectively. Stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC)-based quantitative proteomics was used to analyze the protein expressions of energy metabolic pathways in EOC cells treated with and without ivermectin. Cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, and important molecules in energy metabolism pathway were examined before and after ivermectin treatment of different EOC cells.
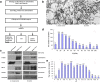
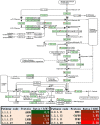
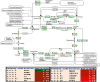
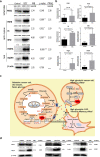
Results: In total, 1198 mtDEPs were identified, and various mtDEPs were related to energy metabolism changes in EOC, with an interesting result that EOC tissues had enhanced abilities in oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), Kreb's cycle, and aerobic glycolysis, for ATP generation, with experiment-confirmed upregulations of UQCRH in OXPHOS; IDH2, CS, and OGDHL in Kreb's cycle; and PKM2 in glycolysis pathways. Importantly, PDHB that links glycolysis with Kreb's cycle was upregulated in EOC. SILAC-based quantitative proteomics found that the protein expression levels of energy metabolic pathways were regulated by ivermectin in EOC cells. Furthermore, ivermectin demonstrated its strong abilities to inhibit proliferation and cell cycle and promote apoptosis in EOC cells, through molecular networks to _target PFKP in glycolysis; IDH2 and IDH3B in Kreb's cycle; ND2, ND5, CYTB, and UQCRH in OXPHOS; and MCT1 and MCT4 in lactate shuttle to inhibit EOC growth.
Conclusions: Our findings revealed that the Warburg and reverse Warburg effects coexisted in human ovarian cancer tissues, provided the first multiomics-based molecular alteration spectrum of ovarian cancer energy metabolism pathways (aerobic glycolysis, Kreb's cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, and lactate shuttle), and demonstrated that the antiparasite drug ivermectin effectively regulated these changed molecules in energy metabolism pathways and had strong capability to inhibit cell proliferation and cell cycle progression and promote cell apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. The observed molecular changes in energy metabolism pathways bring benefits for an in-depth understanding of the molecular mechanisms of energy metabolism heterogeneity and the discovery of effective biomarkers for individualized patient stratification and predictive/prognostic assessment and therapeutic _targets/drugs for personalized therapy of ovarian cancer patients.
Keywords: Aerobic glycolysis; Early diagnosis; Energy metabolism pathway; Epithelial ovarian carcinoma; Ivermectin; Kreb’s cycle; Lactate shuttle; Mitochondrial proteomics; Molecular biomarker pattern; Oxidative phosphorylation; Predictive preventive personalized medicine (PPPM); Prognostic assessment; Reverse Warburg effect; SILAC-based quantitative proteomics; Warburg effect; iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics.
© European Association for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine (EPMA) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The lncRNA SNHG3 regulates energy metabolism of ovarian cancer by an analysis of mitochondrial proteomes.Gynecol Oncol. 2018 Aug;150(2):343-354. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.06.013. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Gynecol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29921511
-
SILAC quantitative proteomics analysis of ivermectin-related proteomic profiling and molecular network alterations in human ovarian cancer cells.J Mass Spectrom. 2021 Jan;56(1):e4659. doi: 10.1002/jms.4659. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Mass Spectrom. 2021. PMID: 33047383
-
Anti-parasite drug ivermectin can suppress ovarian cancer by regulating lncRNA-EIF4A3-mRNA axes.EPMA J. 2020 May 28;11(2):289-309. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00209-y. eCollection 2020 Jun. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 32549918 Free PMC article.
-
MASS SPECTROMETRY-BASED MITOCHONDRIAL PROTEOMICS IN HUMAN OVARIAN CANCERS.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2020 Sep;39(5-6):471-498. doi: 10.1002/mas.21618. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2020. PMID: 32020673 Review.
-
Flavonoids against the Warburg phenotype-concepts of predictive, preventive and personalised medicine to cut the Gordian knot of cancer cell metabolism.EPMA J. 2020 Jul 30;11(3):377-398. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00217-y. eCollection 2020 Sep. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 32843908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kaempferol, a Phytoprogestin, Induces a Subset of Progesterone-Regulated Genes in the Uterus.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 15;15(6):1407. doi: 10.3390/nu15061407. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986136 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis-related gene signature stratifies lower-grade glioma patients and predicts immune characteristics.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 25;13:1036460. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1036460. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36386799 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Identifies Pan-Cancer Landscape of Nrf2 Oxidative Stress Response Pathway-Related Genes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 17;2022:8450087. doi: 10.1155/2022/8450087. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35242279 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarker Identification and Risk Prediction Model Development for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Lung Metastasis Based on Primary Lesion Proteomics.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 15;30(14):3059-3072. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3806. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38723277 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis engages in c-Myc-mediated breast cancer stemness.J Transl Med. 2023 Jun 23;21(1):409. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04204-5. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37353799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith RA, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Brooks D, Doroshenk M, Fedewa S, Saslow D, Brawley OW, Wender R. Cancer screening in the United States, 2015: a review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:30–54. doi: 10.3322/caac.21261. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

