Label-Free and Sensitive Determination of Cadmium Ions Using a Ti-Modified Co3O4-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor
- PMID: 33266040
- PMCID: PMC7761109
- DOI: 10.3390/bios10120195
Label-Free and Sensitive Determination of Cadmium Ions Using a Ti-Modified Co3O4-Based Electrochemical Aptasensor
Abstract
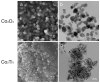
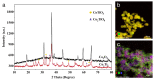
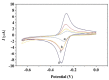
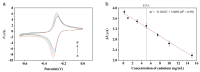
The current work demonstrates an electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive determination of Cd2+ based on the Ti-modified Co3O4 nanoparticles. In this unlabeled system, Ti-modified Co3O4 nanoparticles act as current signal amplifiers modified on the screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) surface, while the derivative aptamer of Cd2+ works as a _target recognizer. In addition, the sensing is based on the increase in electrochemical probe thionine current signal due to the binding of aptamer to Cd2+ via specific recognition. In the current study, key parameters, including aptamer concentration, pH, and incubation time were optimized, respectively, to ensure sensing performance. Cyclic voltammetry was used not only to characterize each preparation and optimization step, but also to profile the bindings of aptamer to Cd2+. Under optimal conditions, Cd2+ can be determined in a linear range of 0.20 to 15 ng/mL, with a detection limit of 0.49 ng/mL, significantly below the maximum concentration limit set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Based on comparative analysis and the results of recovery test with real samples, this simple, label-free but highly selective method has considerable potential and thus can be used as an in-situ environmental monitoring platform for Cd2+ testing.
Keywords: Ti-modified Co3O4; aptamer; cadmium; cyclic voltammetry; electrochemical aptasensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reduced graphene oxide/nile blue/gold nanoparticles complex-modified glassy carbon electrode used as a sensitive and label-free aptasensor for ratiometric electrochemical sensing of dopamine.Anal Chim Acta. 2018 Sep 26;1025:154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.03.036. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Anal Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 29801604
-
Development of a label-free electrochemical aptasensor based on diazonium electrodeposition: Application to cadmium detection in water.Anal Biochem. 2021 Jan 1;612:113956. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2020.113956. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Anal Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32950496
-
Fabrication of a novel aptasensor based on three-dimensional reduced graphene oxide/polyaniline/gold nanoparticle composite as a novel platform for high sensitive and specific cocaine detection.Anal Chim Acta. 2017 Dec 15;996:10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.10.035. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Anal Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 29137703
-
An ultra-sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for simultaneous quantitative detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in fruit and vegetable.Food Chem. 2022 Jul 15;382:132173. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132173. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35149468
-
Recent Aptamer-Based Biosensors for Cd2+ Detection.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;13(6):612. doi: 10.3390/bios13060612. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37366977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Facile Aptasensor for Instantaneous Determination of Cadmium Ions Based on Fluorescence Amplification Effect of MOPS on FAM-Labeled Aptamer.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;11(5):133. doi: 10.3390/bios11050133. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922514 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium Ions' Trace-Level Detection Using a Portable Fiber Optic-Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jul 27;12(8):573. doi: 10.3390/bios12080573. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36004969 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Application of Bionanosensors for the Analysis of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Environments.Molecules. 2023 Dec 20;29(1):34. doi: 10.3390/molecules29010034. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38202619 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afkhami A., Soltani-Felehgari F., Madrakian T., Ghaedi H., Rezaeivala M. Fabrication and application of a new modified electrochemical sensor using nano-silica and a newly synthesized Schiff base for simultaneous determination of Cd2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+ ions in water and some foodstuff samples. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2013;771:21–30. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.02.031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alvarez M.A., Carrillo G. Simultaneous determination of arsenic, cadmium, copper, chromium, nickel, lead and thallium in total digested sediment samples and available fractions by electrothermal atomization atomic absorption spectroscopy (ET AAS) Talanta. 2012;97:505–512. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ashrafzadeh Afshar E., Taher M.A., Fazelirad H. Ultra-trace determination of thallium(I) using a nanocomposite consisting of magnetite, halloysite nanotubes and dibenzo-18-crown-6 for preconcentration prior to its quantitation by ET-AAS. Microchim. Acta. 2017;184:791–797. doi: 10.1007/s00604-016-2040-z. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

