TNF-α-mediated reduction in inhibitory neurotransmission precedes sporadic Alzheimer's disease pathology in young Trem2R47H rats
- PMID: 33434745
- PMCID: PMC7949092
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016395
TNF-α-mediated reduction in inhibitory neurotransmission precedes sporadic Alzheimer's disease pathology in young Trem2R47H rats
Abstract
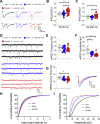
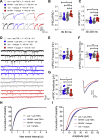
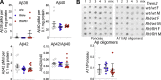
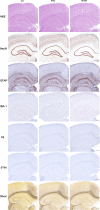
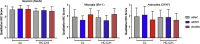
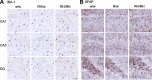
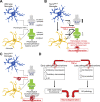
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative dementia associated with deposition of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, formed by amyloid β (Aβ) peptides and phosphor-tau, respectively, in the central nervous system. Approximately 2% of AD cases are due to familial AD (FAD); ∼98% of cases are sporadic AD (SAD). Animal models with FAD are commonly used to study SAD pathogenesis. Because mechanisms leading to FAD and SAD may be distinct, to study SAD pathogenesis, we generated Trem2R47H knock-in rats, which carry the SAD risk factor p.R47H variant of the microglia gene triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2). Trem2R47H rats produce human-Aβ from a humanized-App rat allele because human-Aβ is more toxic than rodent-Aβ and the pathogenic role of the p.R47H TREM2 variant has been linked to human-Aβ-clearing deficits. Using periadolescent Trem2R47H rats, we previously demonstrated that supraphysiological tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) boosts glutamatergic transmission, which is excitatory, and suppresses long-term potentiation, a surrogate of learning and memory. Here, we tested the effect of the p.R47H variant on the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid. We report that GABAergic transmission is decreased in Trem2R47H/R47H rats. This decrease is due to acute and reversible action of TNF-α and is not associated with increased human-Aβ levels and AD pathology. Thus, the p.R47H variant changes the excitatory/inhibitory balance, favoring excitation. This imbalance could potentiate glutamate excitotoxicity and contribute to neuronal dysfunction, enhanced neuronal death, and neurodegeneration. Future studies will determine whether this imbalance represents an early, Aβ-independent pathway leading to dementia and may reveal the AD-modifying therapeutic potential of TNF-α inhibition in the central nervous system.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Aβ; GABA; TNF-α; Trem2; animal model; neurodegenerative disease; rats; synaptic plasticity.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microglia TREM2R47H Alzheimer-linked variant enhances excitatory transmission and reduces LTP via increased TNF-α levels.Elife. 2020 Jun 24;9:e57513. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57513. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32579116 Free PMC article.
-
Trem2 Splicing and Expression are Preserved in a Human Aβ-producing, Rat Knock-in Model of Trem2-R47H Alzheimer's Risk Variant.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 5;10(1):4122. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60800-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32139718 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of pathology, expression and proteomic profiles in human TREM2 variant postmortem brains with and without Alzheimer's disease.Brain Pathol. 2020 Jul;30(4):794-810. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12842. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Brain Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32267026 Free PMC article.
-
Untangling the Role of TREM2 in Conjugation with Microglia in Neuronal Dysfunction: A Hypothesis on a Novel Pathway in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2023;94(s1):S319-S333. doi: 10.3233/JAD-221070. J Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 36683512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TREM2 Function in Alzheimer's Disease and Neurodegeneration.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016 Apr 20;7(4):420-7. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00313. Epub 2016 Feb 19. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26854967 Review.
Cited by
-
NK-cell dysfunction of acute myeloid leukemia in relation to the renin-angiotensin system and neurotransmitter genes.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Sep 20;17(1):1495-1506. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0551. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 36213442 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia as a Hub for Suicide Neuropathology: Future Investigation and Prevention _targets.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 18;16:839396. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.839396. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The brain cytokine orchestra in multiple sclerosis: from neuroinflammation to synaptopathology.Mol Brain. 2024 Jan 23;17(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01077-7. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 38263055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in Alzheimer's disease and neuroprotective effects of pegylated self-assembled nanoscaffolds.Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022 Dec 20;4:100149. doi: 10.1016/j.crphar.2022.100149. eCollection 2023. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov. 2022. PMID: 36593925 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of methadone on the anticonvulsant efficacy of valproate sodium gabapentin against maximal electroshock seizure in mice by regulation of brain MDA TNF-α.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 23;13:920107. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.920107. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36081867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guerreiro R., Wojtas A., Bras J., Carrasquillo M., Rogaeva E., Majounie E., Cruchaga C., Sassi C., Kauwe J.S., Younkin S., Hazrati L., Collinge J., Pocock J., Lashley T., Williams J., Alzheimer Genetic Analysis, G. TREM2 variants in Alzheimer's disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;368:117–127. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou S.L., Tan C.C., Hou X.H., Cao X.P., Tan L., Yu J.T. TREM2 variants and neurodegenerative diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019;68:1171–1184. - PubMed
-
- Wunderlich P., Glebov K., Kemmerling N., Tien N.T., Neumann H., Walter J. Sequential proteolytic processing of the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2 (TREM2) protein by ectodomain shedding and gamma-secretase-dependent intramembranous cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2013;288:33027–33036. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

