Electrochemical Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers for the Aqueous Detection of Biologically Relevant Molecules
- PMID: 33478121
- PMCID: PMC7835872
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11010252
Electrochemical Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers for the Aqueous Detection of Biologically Relevant Molecules
Abstract
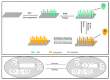
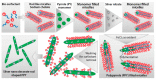
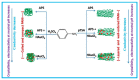
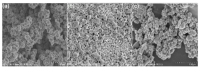
Electrochemical sensors appear as low-cost, rapid, easy to use, and in situ devices for determination of diverse analytes in a liquid solution. In that context, conducting polymers are much-explored sensor building materials because of their semiconductivity, structural versatility, multiple synthetic pathways, and stability in environmental conditions. In this state-of-the-art review, synthetic processes, morphological characterization, and nanostructure formation are analyzed for relevant literature about electrochemical sensors based on conducting polymers for the determination of molecules that (i) have a fundamental role in the human body function regulation, and (ii) are considered as water emergent pollutants. Special focus is put on the different types of micro- and nanostructures generated for the polymer itself or the combination with different materials in a composite, and how the rough morphology of the conducting polymers based electrochemical sensors affect their limit of detection. Polypyrroles, polyanilines, and polythiophenes appear as the most recurrent conducting polymers for the construction of electrochemical sensors. These conducting polymers are usually built starting from bifunctional precursor monomers resulting in linear and branched polymer structures; however, opportunities for sensitivity enhancement in electrochemical sensors have been recently reported by using conjugated microporous polymers synthesized from multifunctional monomers.
Keywords: ascorbic acid; conducting polymers; electrochemical sensors; emergent pollutants; glucose; hydrogen peroxide; neurotransmitters; nitroaromatic compounds; pharmaceuticals; phenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrochemical Sensors Based on Organic Conjugated Polymers.Sensors (Basel). 2008 Jan 9;8(1):118-141. doi: 10.3390/s8010118. Sensors (Basel). 2008. PMID: 27879698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for environmental analysis.Biosens Bioelectron. 2021 Jan 15;172:112719. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112719. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Biosens Bioelectron. 2021. PMID: 33166805 Review.
-
Conducting dyes as electro-active monomers and polymers for detecting analytes in biological and environmental samples.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 7;9(9):e19943. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19943. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conducting polymer-based electrochemical biosensors for neurotransmitters: A review.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Apr 15;102:540-552. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.11.069. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29220802 Review.
-
Application of Conducting Polymer Nanostructures to Electrochemical Biosensors.Molecules. 2020 Jan 12;25(2):307. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020307. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31940924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Biosensors for Pathogen Detection: An Updated Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;12(11):927. doi: 10.3390/bios12110927. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Polypyrrole-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for the Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;13(4):674. doi: 10.3390/nano13040674. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36839042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reagentless electrochemical biosensors through incorporation of unnatural amino acids on the protein structure.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Mar 15;200:113861. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113861. Epub 2021 Dec 7. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 34986438 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer-Magnetic Semiconductor Nanocomposites for Industrial Electronic Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Jun 17;14(12):2467. doi: 10.3390/polym14122467. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydroxyapatite/L-Lysine Composite Coating as Glassy Carbon Electrode Modifier for the Analysis and Detection of Nile Blue A.Materials (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;15(12):4262. doi: 10.3390/ma15124262. Materials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35744321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Si B., Song E. Recent Advances in the Detection of Neurotransmitters. Chemosensors. 2018;6:1. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors6010001. - DOI
-
- Si B., Song E. Molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective detection of multi-analyte neurotransmitters. Microelectron. Eng. 2018;187–188:58–65. doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2017.11.016. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

