Lignans of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): A Comprehensive Review
- PMID: 33562414
- PMCID: PMC7914952
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26040883
Lignans of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.): A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
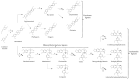
Major lignans of sesame sesamin and sesamolin are benzodioxol--substituted furofurans. Sesamol, sesaminol, its epimers, and episesamin are transformation products found in processed products. Synthetic routes to all lignans are known but only sesamol is synthesized industrially. Biosynthesis of furofuran lignans begins with the dimerization of coniferyl alcohol, followed by the formation of dioxoles, oxidation, and glycosylation. Most genes of the lignan pathway in sesame have been identified but the inheritance of lignan content is poorly understood. Health-promoting properties make lignans attractive components of functional food. Lignans enhance the efficiency of insecticides and possess antifeedant activity, but their biological function in plants remains hypothetical. In this work, extensive literature including historical texts is reviewed, controversial issues are critically examined, and errors perpetuated in literature are corrected. The following aspects are covered: chemical properties and transformations of lignans; analysis, purification, and total synthesis; occurrence in Seseamum indicum and related plants; biosynthesis and genetics; biological activities; health-promoting properties; and biological functions. Finally, the improvement of lignan content in sesame seeds by breeding and biotechnology and the potential of hairy roots for manufacturing lignans in vitro are outlined.
Keywords: biological function; health-promoting properties; lignan biosynthesis; lignan glycosides; plant biotechnology; sesame lignans; sesamin; sesamol; sesamolin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


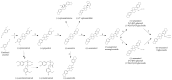
Similar articles
-
(+)-Sesamin-oxidising CYP92B14 shapes specialised lignan metabolism in sesame.Plant J. 2020 Nov;104(4):1117-1128. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14989. Epub 2020 Oct 11. Plant J. 2020. PMID: 32955771 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of infrared heating on the formation of sesamol and quality of defatted flours from Sesamum indicum L.J Food Sci. 2009 May-Jul;74(4):H105-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01132.x. J Food Sci. 2009. PMID: 19490327
-
Oxidative rearrangement of (+)-sesamin by CYP92B14 co-generates twin dietary lignans in sesame.Nat Commun. 2017 Dec 18;8(1):2155. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02053-7. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29255253 Free PMC article.
-
Lignans of sesame: purification methods, biological activities and biosynthesis--a review.Bioorg Chem. 2013 Oct;50:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Bioorg Chem. 2013. PMID: 23933354 Review.
-
The relationship of antioxidant components and antioxidant activity of sesame seed oil.J Sci Food Agric. 2015 Oct;95(13):2571-8. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7035. Epub 2015 Jan 23. J Sci Food Agric. 2015. PMID: 25472416 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypolipidemic and Anti-Atherogenic Effects of Sesamol and Possible Mechanisms of Action: A Comprehensive Review.Molecules. 2023 Apr 19;28(8):3567. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083567. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesamin: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Ameliorating Symptoms of Diabetes.Molecules. 2023 Oct 25;28(21):7255. doi: 10.3390/molecules28217255. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37959677 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic effect of Loranthus parasiticus lignan derivatives on collagen-induced arthritis in rats through the SHBG/NFκB pathway.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Feb;32(1):873-883. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01409-4. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38227094
-
Treatment of High-Polyphenol-Content Waters Using Biotechnological Approaches: The Latest Update.Molecules. 2022 Dec 30;28(1):314. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010314. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesame Extract Promotes Chemopreventive Effect of Hesperidin on Early Phase of Diethylnitrosamine-Initiated Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rats.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 14;13(10):1687. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101687. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34683980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedigian D., Harlan J.R. Evidence for cultivation of sesame in the ancient world. Econ. Bot. 1986;40:137–154. doi: 10.1007/BF02859136. - DOI
-
- Nayar N.M., Mehra K.L. Sesame: Its uses, botany, cytogenetics and origin. Econ. Bot. 1970;24:20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02860629. - DOI
-
- Bedigian D. Evolution of sesame revisited: Domestication, diversity and prospects. Gen. Res. Crop Evol. 2003;50:779–787.
-
- Bedigian D. A New Combination for the Indian Progenitor of Sesame, Sesamum indicum (Pedaliaceae) Novon. 2014;23:5–13. doi: 10.3417/2012062. - DOI
-
- Faostat Food and Agriculture Organization Statistical Databases. [(accessed on 13 July 2019)];2016 Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

