BiVO4/Fe3O4@polydopamine superparticles for tumor multimodal imaging and synergistic therapy
- PMID: 33781296
- PMCID: PMC8008624
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-00802-x
BiVO4/Fe3O4@polydopamine superparticles for tumor multimodal imaging and synergistic therapy
Abstract
Background: Despite tremendous progress has been achieved in tumor theranostic over the past decade, accurate identification and complete eradication of tumor cells remain a great challenge owing to the limitation of single imaging modality and therapeutic strategy.
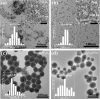
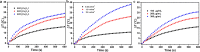
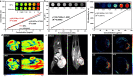
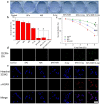
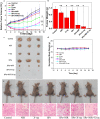
Results: Herein, we successfully design and construct BiVO4/Fe3O4@polydopamine (PDA) superparticles (SPs) for computed tomography (CT)/photoacoustic (PA)/magnetic resonance (MR) multimodal imaging and radiotherapy (RT)/photothermal therapy (PTT) synergistic therapy toward oral epithelial carcinoma. On the one hand, BiVO4 NPs endow BiVO4/Fe3O4@PDA SPs with impressive X-ray absorption capability due to the high X-ray attenuation coefficient of Bi, which is beneficial for their utilization as radiosensitizers for CT imaging and RT. On the other hand, Fe3O4 NPs impart BiVO4/Fe3O4@PDA SPs with the superparamagnetic property as a T2-weighted contrast agent for MR imaging. Importantly, the aggregation of Fe3O4 NPs in SPs and the presence of PDA shell greatly improve the photothermal conversion capability of SPs, making BiVO4/Fe3O4@PDA SPs as an ideal photothermal transducer for PA imaging and PTT. By integrating advantages of various imaging modalities (CT/PA/MR) and therapeutic strategies (RT/PTT), our BiVO4/Fe3O4@PDA SPs exhibit the sensitive multimodal imaging feature and superior synergistic therapeutic efficacy on tumors.
Conclusions: Since there are many kinds of building blocks with unique properties appropriating for self-assembly, our work may largely enrich the library of nanomateirals for tumor diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: BiVO4 nanoparticles; Fe3O4 nanoparticles; Multimodal imaging; Superparticles; Synergy therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fe3O4@polydopamine Composite Theranostic Superparticles Employing Preassembled Fe3O4 Nanoparticles as the Core.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016 Sep 7;8(35):22942-52. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b07997. Epub 2016 Aug 25. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016. PMID: 27560801
-
Integration of Fe3O4 with Bi2S3 for Multi-Modality Tumor Theranostics.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 May 20;12(20):22650-22660. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c05088. Epub 2020 May 6. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32330380
-
_targeted polydopamine nanoparticles enable photoacoustic imaging guided chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of tumor.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 1;47:124-134. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27721008
-
Polydopamine-Based Nanoparticles for Photothermal Therapy/Chemotherapy and their Synergistic Therapy with Autophagy Inhibitor to Promote Antitumor Treatment.Chem Rec. 2021 Apr;21(4):781-796. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202000170. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Chem Rec. 2021. PMID: 33634962 Review.
-
Theranostics Based on Iron Oxide and Gold Nanoparticles for Imaging- Guided Photothermal and Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(16):1858-1871. doi: 10.2174/1568026617666161122120537. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27875977 Review.
Cited by
-
PDA-Based Drug Delivery Nanosystems: A Potential Approach for Glioma Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Aug 30;17:3751-3775. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S378217. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36065287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D modeling of in vivo MRI-guided nano-photothermal therapy mediated by magneto-plasmonic nanohybrids.Biomed Eng Online. 2023 Aug 1;22(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12938-023-01131-w. Biomed Eng Online. 2023. PMID: 37528482 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for NIR-Induced Photothermal Therapy of Potential Application in Cervical Cancer.ACS Omega. 2023 Jun 8;8(24):21793-21801. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01374. eCollection 2023 Jun 20. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37360441 Free PMC article.
-
New anti-cancer explorations based on metal ions.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Oct 23;20(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01661-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36274142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization system based on hierarchical _targeting for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Aug 22;16:100398. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100398. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36081579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atun R, Jaffray DA, Barton MB, Bray F, Baumann M, Vikram B, Hanna TP, Knaul FM, Lievens Y, Lui TYM, Milosevic M, O’Sullivan B, Rodin DL, Rosenblatt E, Van DJ, Yap ML, Zubizarreta E, Gospodarowicz M. Expanding global access to radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:1153–86. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00222-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

