Development of machine learning model for diagnostic disease prediction based on laboratory tests
- PMID: 33828178
- PMCID: PMC8026627
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-87171-5
Development of machine learning model for diagnostic disease prediction based on laboratory tests
Abstract
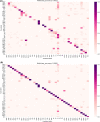
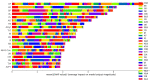
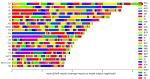
The use of deep learning and machine learning (ML) in medical science is increasing, particularly in the visual, audio, and language data fields. We aimed to build a new optimized ensemble model by blending a DNN (deep neural network) model with two ML models for disease prediction using laboratory test results. 86 attributes (laboratory tests) were selected from datasets based on value counts, clinical importance-related features, and missing values. We collected sample datasets on 5145 cases, including 326,686 laboratory test results. We investigated a total of 39 specific diseases based on the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) codes. These datasets were used to construct light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) ML models and a DNN model using TensorFlow. The optimized ensemble model achieved an F1-score of 81% and prediction accuracy of 92% for the five most common diseases. The deep learning and ML models showed differences in predictive power and disease classification patterns. We used a confusion matrix and analyzed feature importance using the SHAP value method. Our new ML model achieved high efficiency of disease prediction through classification of diseases. This study will be useful in the prediction and diagnosis of diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deep learning assisted detection of glaucomatous optic neuropathy and potential designs for a generalizable model.PLoS One. 2020 May 14;15(5):e0233079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233079. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32407355 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of machine learning diagnostic models for cardiovascular pan-disease based on blood routine and biochemical detection data.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Sep 28;23(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02439-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39342281 Free PMC article.
-
Use of extreme gradient boosting, light gradient boosting machine, and deep neural networks to evaluate the activity stage of extraocular muscles in thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Jan;262(1):203-210. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06256-1. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37773288
-
Artificial intelligence: Deep learning in oncological radiomics and challenges of interpretability and data harmonization.Phys Med. 2021 Mar;83:108-121. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2021.03.009. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Phys Med. 2021. PMID: 33765601 Review.
-
Reviewing ensemble classification methods in breast cancer.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Aug;177:89-112. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.05.019. Epub 2019 May 20. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31319964 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Prediction of Chronic Diseases Using Machine Learning Approach.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Feb 25;2022:2826127. doi: 10.1155/2022/2826127. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35251563 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Machine-Learning Model to Predict COVID-19 Mortality: Application of Ensemble Model and Regarding Feature Impacts.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Jun 14;12(6):1464. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061464. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741274 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning for Patient-Based Real-Time Quality Control (PBRTQC), Analytical and Preanalytical Error Detection in Clinical Laboratory.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 20;14(16):1808. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14161808. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of blood demand prediction model using artificial intelligence based on national public big data.Digit Health. 2024 Jan 17;10:20552076231224245. doi: 10.1177/20552076231224245. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 38250146 Free PMC article.
-
Developing an AI-based prediction model for anaphylactic shock from injection drugs using Japanese real-world data and chemical structure-based analysis.Daru. 2024 Jun;32(1):253-262. doi: 10.1007/s40199-024-00511-4. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Daru. 2024. PMID: 38580799
References
-
- Min S, Lee B, Yoon S. Deep learning in bioinformatics. Brief. Bioinform. 2017;18:851–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

