Predictors of 30-Day Unplanned Readmission After Carotid Artery Stenting Using Artificial Intelligence
- PMID: 33834355
- PMCID: PMC8190015
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-021-01709-7
Predictors of 30-Day Unplanned Readmission After Carotid Artery Stenting Using Artificial Intelligence
Abstract
Introduction: This study aimed to describe the rates and causes of unplanned readmissions within 30 days following carotid artery stenting (CAS) and to use artificial intelligence machine learning analysis for creating a prediction model for short-term readmissions. The prediction of unplanned readmissions after index CAS remains challenging. There is a need to leverage deep machine learning algorithms in order to develop robust prediction tools for early readmissions.
Methods: Patients undergoing inpatient CAS during the year 2017 in the US Nationwide Readmission Database (NRD) were evaluated for the rates, predictors, and costs of unplanned 30-day readmission. Logistic regression, support vector machine (SVM), deep neural network (DNN), random forest, and decision tree models were evaluated to generate a robust prediction model.
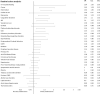
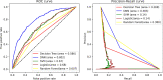
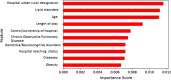
Results: We identified 16,745 patients who underwent CAS, of whom 7.4% were readmitted within 30 days. Depression [p < 0.001, OR 1.461 (95% CI 1.231-1.735)], heart failure [p < 0.001, OR 1.619 (95% CI 1.363-1.922)], cancer [p < 0.001, OR 1.631 (95% CI 1.286-2.068)], in-hospital bleeding [p = 0.039, OR 1.641 (95% CI 1.026-2.626)], and coagulation disorders [p = 0.007, OR 1.412 (95% CI 1.100-1.813)] were the strongest predictors of readmission. The artificial intelligence machine learning DNN prediction model has a C-statistic value of 0.79 (validation 0.73) in predicting the patients who might have all-cause unplanned readmission within 30 days of the index CAS discharge.
Conclusions: Machine learning derived models may effectively identify high-risk patients for intervention strategies that may reduce unplanned readmissions post carotid artery stenting.
Central illustration: Figure 2: ROC and AUPRC analysis of DNN prediction model with other classification models on 30-day readmission data for CAS subjects.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Carotid artery stenting; Machine learning; Readmission.
Plain language summary
We present a novel deep neural network-based artificial intelligence prediction model to help identify a subgroup of patients undergoing carotid artery stenting who are at risk for short-term unplanned readmissions. Prior studies have attempted to develop prediction models but have used mainly logistic regression models and have low prediction ability. The novel model presented in this study boasts 79% capability to accurately predict individuals for unplanned readmissions post carotid artery stenting within 30 days of discharge.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The utilization of artificial neural networks for the prediction of 90-day unplanned readmissions following total knee arthroplasty.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Jun;143(6):3279-3289. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04566-3. Epub 2022 Aug 7. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 35933638
-
Comparison of 30-day readmission rates and risk factors between carotid artery stenting and endarterectomy.J Vasc Surg. 2017 Nov;66(5):1432-1444.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.05.097. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Vasc Surg. 2017. PMID: 28865979
-
Using machine learning to predict paediatric 30-day unplanned hospital readmissions: a case-control retrospective analysis of medical records, including written discharge documentation.Aust Health Rev. 2021 Jun;45(3):328-337. doi: 10.1071/AH20062. Aust Health Rev. 2021. PMID: 33840419
-
Novel Machine Learning Approach for the Prediction of Hernia Recurrence, Surgical Complication, and 30-Day Readmission after Abdominal Wall Reconstruction.J Am Coll Surg. 2022 May 1;234(5):918-927. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000141. J Am Coll Surg. 2022. PMID: 35426406 Review.
-
Causes and prevalence of unplanned readmissions after colorectal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Jul;61(7):1175-81. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12307. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013. PMID: 23730901 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and Outcomes of Clinical Trials on Gene Therapy in Noncongenital Cardiovascular Diseases: Cross-sectional Study of Three Clinical Trial Registries.JMIR Form Res. 2022 Apr 21;6(4):e33893. doi: 10.2196/33893. JMIR Form Res. 2022. PMID: 35451992 Free PMC article.
-
Disease and Economic Burden Associated with Recurrent Pericarditis in a Privately Insured United States Population.Adv Ther. 2021 Oct;38(10):5127-5143. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01868-7. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34417724 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive modeling for COVID-19 readmission risk using machine learning algorithms.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022 May 20;22(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12911-022-01880-z. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2022. PMID: 35596167 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and Diagnosis-Based Trends for Unplanned Pediatric Rehospitalizations in the United States.Cureus. 2021 Dec 5;13(12):e20181. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20181. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35004005 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Hypertension on the Severity of COVID-19: A Review.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 1;78(5):e648-e655. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001116. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34321401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonati LH, Lyrer P, Ederle J, Featherstone R, Brown MM. Percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty and stenting for carotid artery stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;2012:CD000515. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

