_targeting cell-cycle machinery in cancer
- PMID: 33891890
- PMCID: PMC8206013
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.03.010
_targeting cell-cycle machinery in cancer
Abstract
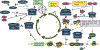
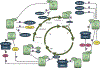
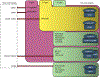
Abnormal activity of the core cell-cycle machinery is seen in essentially all tumor types and represents a driving force of tumorigenesis. Recent studies revealed that cell-cycle proteins regulate a wide range of cellular functions, in addition to promoting cell division. With the clinical success of CDK4/6 inhibitors, it is becoming increasingly clear that _targeting individual cell-cycle components may represent an effective anti-cancer strategy. Here, we discuss the potential of inhibiting different cell-cycle proteins for cancer therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests P.S. has been a consultant at Novartis, Genovis, Guidepoint, The Planning Shop, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Cedilla Therapeutics, Syros Pharmaceuticals and Exo Therapeutics; his laboratory received research funding from Novartis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CDK4 and CDK6 kinases: From basic science to cancer therapy.Science. 2022 Jan 14;375(6577):eabc1495. doi: 10.1126/science.abc1495. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Science. 2022. PMID: 35025636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
_targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From Discovery to Therapy.Cancer Discov. 2016 Apr;6(4):353-67. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0894. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Cancer Discov. 2016. PMID: 26658964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclin D-CDK4/6 functions in cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2020;148:147-169. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Adv Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32723562 Review.
-
Molecular Pathways: _targeting the Cyclin D-CDK4/6 Axis for Cancer Treatment.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jul 1;21(13):2905-10. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0816. Epub 2015 May 4. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25941111 Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jan;48(1):915-925. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-06100-3. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33409716 Review.
Cited by
-
Eupalinolide A induces autophagy via the ROS/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo.Int J Oncol. 2022 Nov;61(5):131. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2022.5421. Epub 2022 Sep 16. Int J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36111510 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Enhancement of Antitumor Effects by Combining Abemaciclib with Desipramine.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 5;25(13):7407. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137407. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000513 Free PMC article.
-
PKMYT1 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression by abrogating AKT1 activity.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023 Feb;46(1):195-209. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00744-y. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2023. PMID: 36350496
-
Anticancer effects of OSW-1 on glioma cells via regulation of the PI3K/AKT signal pathway: A network pharmacology approach and experimental validation in vitro and in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 5;13:967141. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.967141. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36133816 Free PMC article.
-
The yin and yang of chromosomal instability in prostate cancer.Nat Rev Urol. 2024 Jun;21(6):357-372. doi: 10.1038/s41585-023-00845-9. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Nat Rev Urol. 2024. PMID: 38307951 Review.
References
-
- Alvarez-Fernandez M, and Malumbres M (2020). Mechanisms of Sensitivity and Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition. Cancer Cell 37, 514–529. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

