Assessment of hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA in high and low viremic chronic hepatitis B patients
- PMID: 34027120
- PMCID: PMC8122096
- DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2021.104472
Assessment of hepatitis B virus pregenomic RNA in high and low viremic chronic hepatitis B patients
Abstract
Aim of the study: Intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) is the main cause of hepatitis B virus (HBV) persistence. Therefore, a noninvasive serum biomarker that can reflect intrahepatic cccDNA is required for evaluation of HBV virological, biochemical activity and therapeutic response. Aim of the study was to assess serum hepatitis B pregenomic RNA in low viremia patients (HBV DNA < 2000 IU/ml) and high viremia (HBV DNA > 2000 IU/ml).
Material and methods: This study was carried out on two groups of chronic hepatitis B patients: group A - 40 patients with low viremia (HBV DNA < 2000 IU/ml); group B - 40 patients with high viremia (HBV DNA > 2000 IU/ml when diagnosed). They were assessed before treatment and after 6 months of treatment (entecavir 0.5 mg/24 h). Serum HBV pregenomic RNA was quantified using RT-PCR.
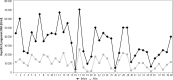
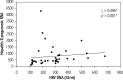
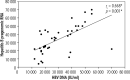
Results: Pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) was significantly lower in group A than in group B (before treatment). Moreover, it was significantly lower after 6 months of treatment than before treatment in group B. A significant positive correlation was observed between pgRNA and HBV DNA in groups A and B (before treatment); however, after 6 months of treatment of group B patients, although 35 patients had undetectable HBV DNA, they showed detectable levels of serum pgRNA and pgRNA > 4000 IU/ml was associated with virological and biochemical activity.
Conclusions: Serum HBV pregenomic RNA might be a promising marker for assessment of HBV virological, biochemical activity and evaluating therapeutic responses.
Keywords: HBV cccDNA; HBV pregenomic RNA; biomarker; entecavir; noninvasive.
Copyright © 2021 Clinical and Experimental Hepatology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic Value of Detection of Pregenomic RNA in Sera of Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients with Different Clinical Outcomes.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Jan 28;58(2):e01275-19. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01275-19. Print 2020 Jan 28. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31723011 Free PMC article.
-
Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients.J Hepatol. 2019 Apr;70(4):615-625. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.11.030. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30529504
-
Serum hepatitis B virus RNA detectability, composition and clinical significance in patients with ab initio hepatitis B e antigen negative chronic hepatitis B.Virol J. 2022 Jan 29;19(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01749-7. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 35093105 Free PMC article.
-
Progression and status of antiviral monitoring in patients with chronic hepatitis B: From HBsAg to HBV RNA.World J Hepatol. 2018 Sep 27;10(9):603-611. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i9.603. World J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30310538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential use of serum HBV RNA in antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B in the era of nucleos(t)ide analogs.Front Med. 2017 Dec;11(4):502-508. doi: 10.1007/s11684-017-0590-z. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Front Med. 2017. PMID: 29170915 Review.
References
-
- Spinall EJ, Hawkins G, Fraser A, et al. . Hepatitis B prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care. Occup Med (Lond) 2011; 61: 531-540. - PubMed
-
- Levrero M, Pollicino T, Petersen J, et al. . Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2009; 51: 581-592. - PubMed
-
- Rehermann B, Ferrari C, Pasquinelli C, et al. . The hepatitis B virus persists for decades after patients’ recovery from acute viral hepatitis despite active maintenance of a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response. Nat Med 1996; 2: 1104-1108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
