Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spondias mombin Extract and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Biofilm-Producing Bacteria
- PMID: 34063685
- PMCID: PMC8124889
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26092681
Green Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Spondias mombin Extract and Their Antimicrobial Activity against Biofilm-Producing Bacteria
Abstract
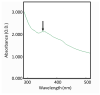
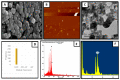
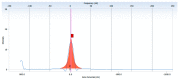
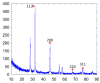
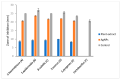
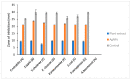
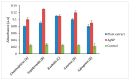
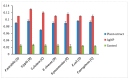
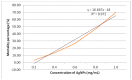
Multidrug resistant bacteria create a challenging situation for society to treat infections. Multidrug resistance (MDR) is the reason for biofilm bacteria to cause chronic infection. Plant-based nanoparticles could be an alternative solution as potential drug candidates against these MDR bacteria, as many plants are well known for their antimicrobial activity against pathogenic microorganisms. Spondias mombin is a traditional plant which has already been used for medicinal purposes as every part of this plant has been proven to have its own medicinal values. In this research, the S. mombin extract was used to synthesise AgNPs. The synthesized AgNPs were characterized and further tested for their antibacterial, reactive oxygen species and cytotoxicity properties. The characterization results showed the synthesized AgNPs to be between 8 to 50 nm with -11.52 of zeta potential value. The existence of the silver element in the AgNPs was confirmed with the peaks obtained in the EDX spectrometry. Significant antibacterial activity was observed against selected biofilm-forming pathogenic bacteria. The cytotoxicity study with A. salina revealed the LC50 of synthesized AgNPs was at 0.81 mg/mL. Based on the ROS quantification, it was suggested that the ROS production, due to the interaction of AgNP with different bacterial cells, causes structural changes of the cell. This proves that the synthesized AgNPs could be an effective drug against multidrug resistant bacteria.
Keywords: AgNP; Spondias mombin; biofilm bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibacterial activities of hexadecanoic acid methyl ester and green-synthesized silver nanoparticles against multidrug-resistant bacteria.J Basic Microbiol. 2021 Jun;61(6):557-568. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202100061. Epub 2021 Apr 19. J Basic Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33871873
-
Implementation of Silver Nanoparticles Green Synthesized with Leaf Extract of Coccinia grandis as Antimicrobial Agents Against Head and Neck Infection MDR Pathogens.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(17):2312-2325. doi: 10.2174/0113892010290653240109053852. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38347796
-
Exploration of reducing and stabilizing phytoconstituents in Arisaema dracontium extract for the effective synthesis of Silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their antibacterial and toxicological proprties.Microb Pathog. 2024 Jul;192:106711. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106711. Epub 2024 May 23. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38788810
-
Antibacterial and antibiofilm potential of silver nanoparticles against antibiotic-sensitive and multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.Braz J Microbiol. 2021 Mar;52(1):267-278. doi: 10.1007/s42770-020-00406-x. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Braz J Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33231865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles as Silver Lining in Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review.Curr Drug Deliv. 2022;19(2):170-181. doi: 10.2174/1567201818666210331123022. Curr Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 33797368 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological and Photocatalytic Activities of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from the Leaf Extract of Euphorbia royleana Boiss.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(35):2813-2827. doi: 10.2174/0113816128319010240730115613. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39129154
-
Current Knowledge on the Oxidative-Stress-Mediated Antimicrobial Properties of Metal-Based Nanoparticles.Microorganisms. 2022 Feb 14;10(2):437. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020437. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35208891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial Efficacy of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Salvia nubicola Extract against Ralstonia solanacearum, the Causal Agent of Vascular Wilt of Tomato.ACS Omega. 2023 Aug 17;8(34):31155-31167. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03164. eCollection 2023 Aug 29. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37663485 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plants extract and their bio-medical applications.Heliyon. 2024 May 1;10(11):e29766. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29766. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38828360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Mahonia fortunei extracts and characterization of its inhibitory effect on Chinese cabbage soft rot pathogen.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1030261. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1030261. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garibo D., Borbón-Nuñez H.A., De León J.N.D., Mendoza E.G., Estrada I., Toledano-Magaña Y., Tiznado H., Ovalle-Marroquin M., Soto-Ramos A.G., Blanco A., et al. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Lysiloma acapulcensis exhibit high-antimicrobial activity. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69606-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chinni S., Gopinath S., Anbu P., Fuloria N., Fuloria S., Mariappan P., Krusnamurthy K., Reddy L.V., Ramachawolran G., Sreeramanan S., et al. Characterization and Antibacterial Response of Silver Nanoparticles Biosynthesized Using an Ethanolic Extract of Coccinia indica Leaves. Crystals. 2021;11:97. doi: 10.3390/cryst11020097. - DOI
-
- Das C.G., Kumar G., Dhas S., Velu K., Govindaraju K., Joselin J., Baalamurugan J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (biosynthe-sis): A short review on recent advances. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020;27:101593. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101593. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

