Non-cationic Material Design for Nucleic Acid Delivery
- PMID: 34164572
- PMCID: PMC8218910
- DOI: 10.1002/adtp.201900206
Non-cationic Material Design for Nucleic Acid Delivery
Abstract
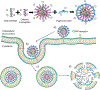
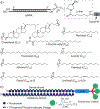
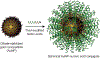
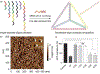
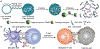
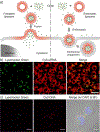
Nucleic acid delivery provides effective options to control intracellular gene expression and protein production. Efficient delivery of nucleic acid typically requires delivery vehicles to facilitate the entry of nucleic acid into cells. Among non-viral delivery vehicles, cationic materials are favored because of their high loading capacity of nucleic acids and prominent cellular uptake efficiency through electrostatic interaction. However, cationic moieties at high dosage tend to induce severe cytotoxicity due to the interference on cell membrane integrity. In contrast, non-cationic materials present alternative delivery approaches with less safety concerns than cationic materials. In this Progress Report, principles of non-cationic material design for nucleic acid delivery are discussed. Examples of such non-cationic platforms are highlighted, including complexation or conjugation with nucleic acids and self-assembled nucleic acid structures.
Keywords: Nucleic acid delivery; material design; non-cationic; non-viral.
Figures
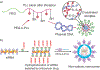
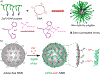
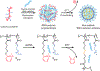
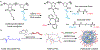
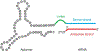
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in nonviral vectors for gene delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):971-9. doi: 10.1021/ar200151m. Epub 2011 Aug 26. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 21870813 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide vectors for the nonviral delivery of nucleic acids.Acc Chem Res. 2012 Jul 17;45(7):1048-56. doi: 10.1021/ar2002304. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Acc Chem Res. 2012. PMID: 22455499
-
Assessing Nucleic Acid: Cationic Nanoparticle Interaction for Gene Delivery.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2211:43-55. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0943-9_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33336269
-
Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles Mediated Nucleic Acids Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 28;18:8001-8021. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S433737. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38164266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cationic Polymers as Transfection Reagents for Nucleic Acid Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 15;15(5):1502. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051502. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242744 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances and Prospects of Nucleic Acid Therapeutics for Anti-Cancer Therapy.Molecules. 2024 Oct 7;29(19):4737. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194737. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Applications of Nanomedicine: Recent Developments and Future Perspectives.Molecules. 2024 Apr 30;29(9):2073. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092073. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA Delivery: Challenges and Advances through Polymeric Soft Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1739. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031739. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Viral Carriers for Nucleic Acids Delivery: Fundamentals and Current Applications.Life (Basel). 2023 Mar 29;13(4):903. doi: 10.3390/life13040903. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37109432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CES1-Triggered Liver-Specific Cargo Release of CRISPR/Cas9 Elements by Cationic Triadic Copolymeric Nanoparticles _targeting Gene Editing of PCSK9 for Hyperlipidemia Amelioration.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jul;10(19):e2300502. doi: 10.1002/advs.202300502. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37083231 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
